DATE
Description
DATE provides operations related to formatting or manipulating a date. To use this Nexial expression, one would start by specifying a DATE instance with one of the following:
[DATE({date}) => ... ...]- start a new DATE instance using standard date formatMM/dd/yyyy HH:mm:ss. For example,[DATE(04/01/2017 05:43:11) => ...])starts a Nexial expression on a date of April 1st, 2017 5:43:11 AM.[DATE(now) => ... ...]or[DATE(right now) => ... ...]- start a new DATE instance assuming standard date formatMM/dd/yyyy HH:mm:ssand using current date/time.[DATE({date},{format}) => ... ...]- start a new DATE instance using the specified date format. The date/time formatting follows the standard Java date/time convention. For example,[DATE(2017/04/01,yyyy/MM/dd) => ...]starts a Nexial expression on a date of April 1st, 2017. Technically such date is implicitly set to a time of 00:00:00.[DATE({date},epoch) => ... ...]- start a new DATE instance assuming the specified date value is an epoch (or timestamp).
Operations
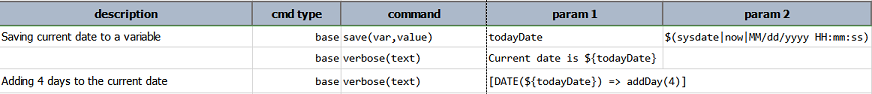
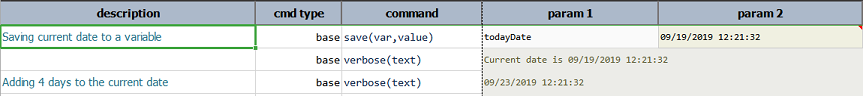
addDay(days)
Add days to the current day part of the date instance.
Example
Script
Output
addHour(hours)
Add hours to the current hour part of the date instance. Note that the value represents
Example
Script

Output

addMinute(minutes)
Add minutes to the current minute part of the date instance.
Example
Script

Output

addMonth(months)
Add months to the current month part of the date instance.
Example
Script

Output

addSecond(seconds)
Add seconds to the current second part of the date instance.
Example
Script

Output

addYear(years)
Add years to the current year part of the date instance.
Example
Script

Output

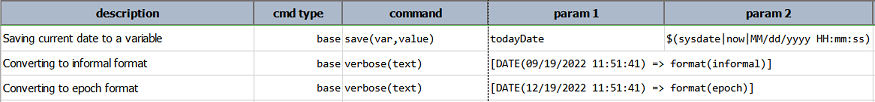
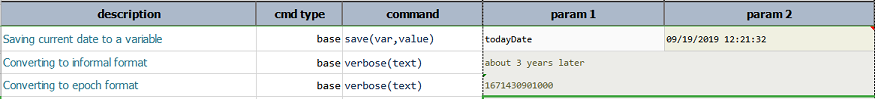
format(pattern)
Transform the same date instance into another textual form, using the specified pattern.
Use epoch to format date as timestamp. Use informal to format date in colloquial, non-exact manner that mimic human
conversation. For example, informal format would output about a minute ago instead of 00:00:57, or about a month and a
half ago rather than 2018/08/24 00:01:32. The informal format is suitable to use in conjunction with the
sound » speak(text) command.
Example
Script
Output
setDay(days)
Set the day part of the date instance.
Example
Script

Output

setDOW(days)
Set the day of the week part of the date instance. Use the numeric value mapped to the day of the week: 1=SUNDAY, 2=MONDAY, 3=TUESDAY, 4=WEDNESDAY, 5=THURSDAY, 6=FRIDAY, 7=SATURDAY.
Example
Script

Output

setHour(hours)
Set the hour part of the date instance. Note that the value represents the 24-hour system (i.e. 22 means 10 p.m.).
Example
Script

Output

setMinute(minutes)
Set the minute part of the date instance.
Example
Script

Output

setMonth(months)
Set the month part of the date instance.
Example
Script

Output

setSecond(seconds)
Set the second part of the date instance.
Example
Script

Output

setYear(years)
Set the year part of the date instance.
Example
Script

Output

store(var)
Save current DATE expression to a data variable. If the specified var exists, its value will be overwritten. Using this operation, one can put an expression on pause and resume it at a later time.
Example
Script

Output

text
Transform the date instance to its textual form, which would most likely be the way it was initially specified.
Example
Script

Output
