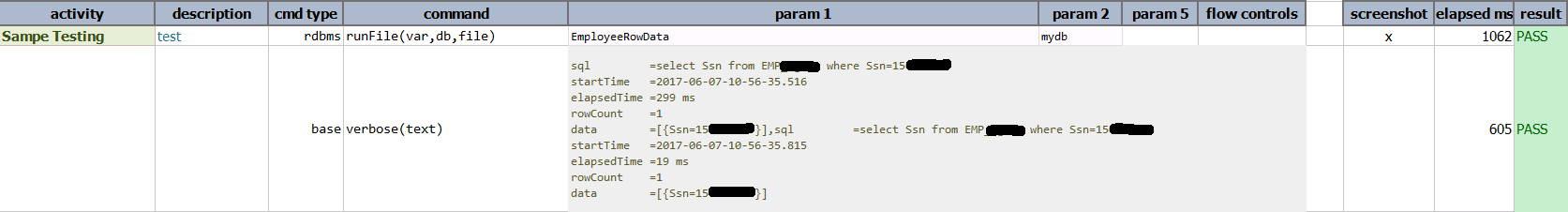
rdbms » runFile(var,db,file)
Description
This command executes a series of SQL statements. The difference between this command and
runSQLs(var,db,sqls) is that this command uses an external file for all the SQL
statements to execute, while runSQLs(var,db,sqls) expects all the SQL statements to be
specified as a parameter. Other than that, both commands have the same capabilities, namely:
- Execute one or more SQL statements, which can be a mixed of INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE, SELECT and EXEC stored procedures.
- Token substitution within the SQLs are carried out prior to execution. For example, the last SQL statement
below has a variable specified -
${client}. This variable will be replaced by its associated value prior to execution.
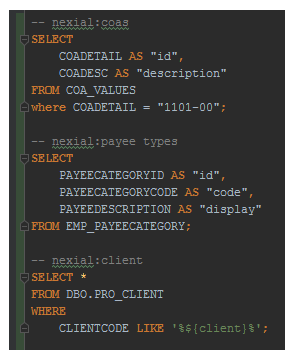
- Separate variable binding per SQL statement. One can indicate a variable name (as part of comment) for each
SQL statement, which will instruct Nexial to assign the associated execution result to such variable. Using the
example above,
- The result of the first SQL will be assigned to the variable
${coas}. - The result of the second SQL will be assigned to the variable
${payee types}. - The result of the third SQL will be assigned to the variable
${client}. The variable will contain the same properties as perrunSQL(var,db,sql). SeeWorking with Execution Resultfor more details.
- The result of the first SQL will be assigned to the variable
- These SQL statements can potentially be committed or rolled back as a single transaction (single unit of work). To
enforce single transaction,
<connection name>.autocommitmust be set tofalse.
Parameters
- var - this parameter is to store result of the sql query into variable.
- db - this parameter is name of the database defined in data file.
- file - this parameter is the location and the file name where are all sql statement are kept.
Consider using
syspathin order to keep all test artifacts in same or similar directory structure.
Example
Script:

Output: