XML
Description
XML Expression provides transformational operations on a XML document.
Operations
append(xpath,content)
search against specified xml via xpath, and append content to all matching instances.
Example
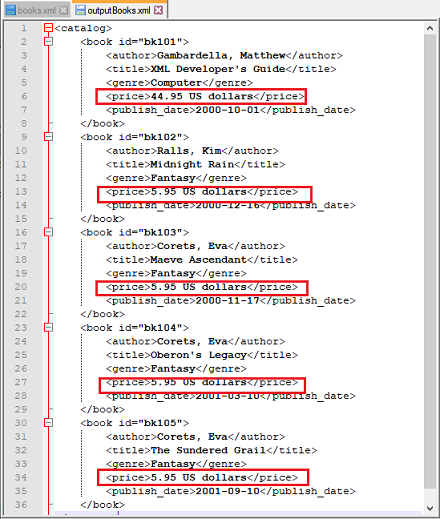
Input XML file:

Script: Append the string " US dollars " to the price in each node

Output file:
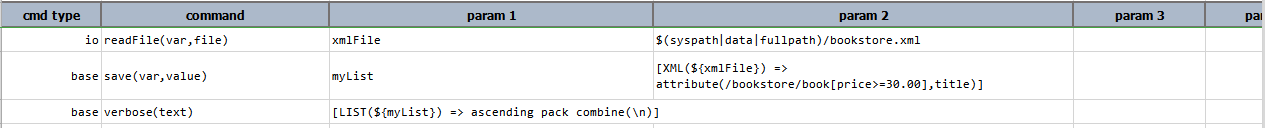
attribute(xpath,name)
Retrieves the value of name attribute from the element(s) that matched the specified xpath. If exactly one match is
found, this operation returns a TEXT data type. If more than one matches are found, a
LIST data type is returned instead.
Example
Input XML file: bookstore.xml
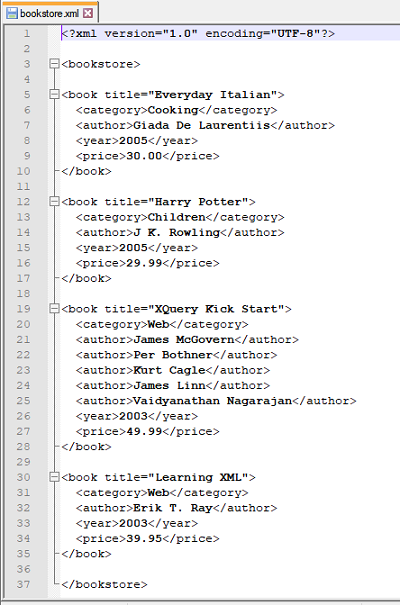
Script: List all titles with price > 30.00
Output:

beautify
“Pretty” formatting on current XML document to improve readability.
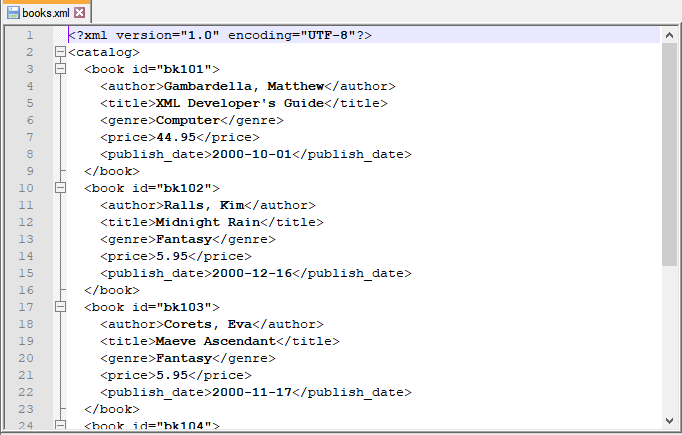
Input XML file: books.xml
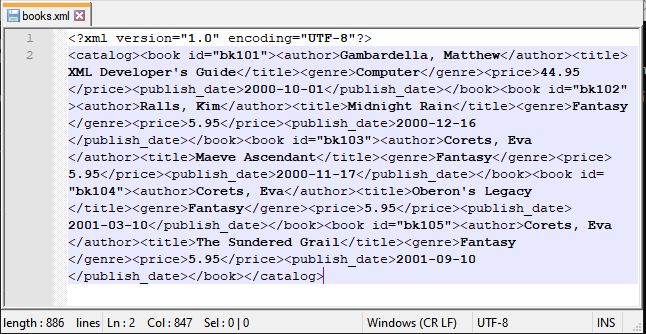
Script: Beautify the above xml

Output file
clear(xpath)
Search against specified xml via xpath and clear content of all matching instances. As seen above, clear(xpath)
clears the element’s content. This is different from delete(xpath) which removes the matching element
itself.
Example
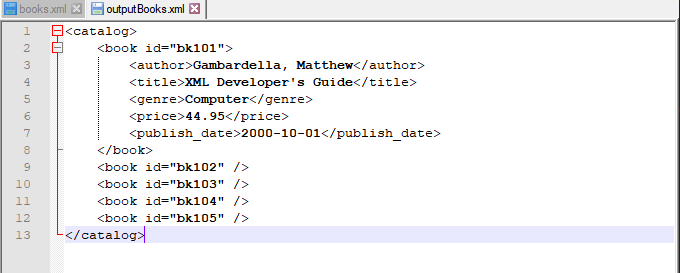
Input XML file: books.xml

Script: Clear all instances where genre is Fantasy.

Output file:
content(xpath)
Retrieves the content of the element(s) that matched the specified xpath. If exactly one match is found, this
operation returns a TEXT data type. If more than one matches are found, a LIST
data type is returned instead.
Example
Input XML file: books.xml

Script: List all the titles.
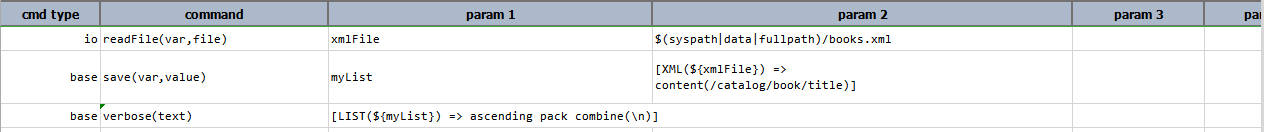
Output:

count(xpath)
Counts the number of elements present at the specified xpath.
Example
Input XML file: bookstore.xml

Script: Count all the books from year 2003.

Output:

delete(xpath)
Search against specified xml via xpath and delete xml node of all matching instances.delete(xpath) removes the
matching element(s) itself. This is different from clear(xpath) which only clears the content of the
matching element(s). This operation is the same as remove(xpath).
Example
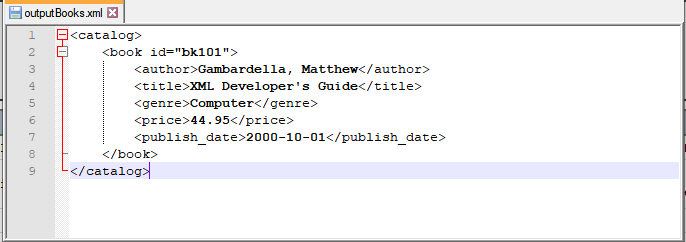
Input XML file: books.xml

Script: Clear the nodes where genre is Fantasy.

Output File:
extract(xpath)
Extract a portion of the XML document based on the specified xpath. Based on the XML document in question and the xpath
specified, the result could either be null (none matched), text (matched to a textual value), XML node or an XML array.
extracted is added as the root tag if the specified xpath matches with multiple nodes in order to make it a valid XML.
Example
1. Extracting XML nodes
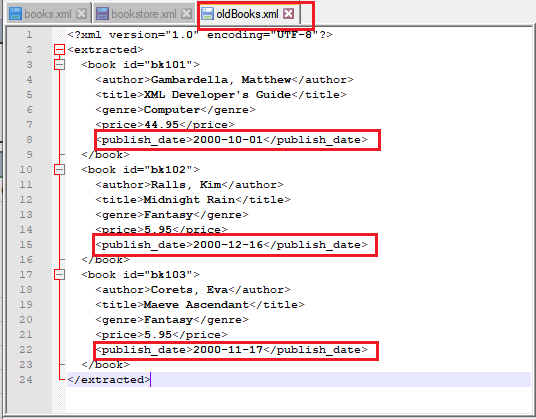
Input XML file: books.xml

Script: Extract all the books published in the year 2000.

Output File:

2. Extracting text and arrays from XML
Input XML file: desserts.xml

Script:
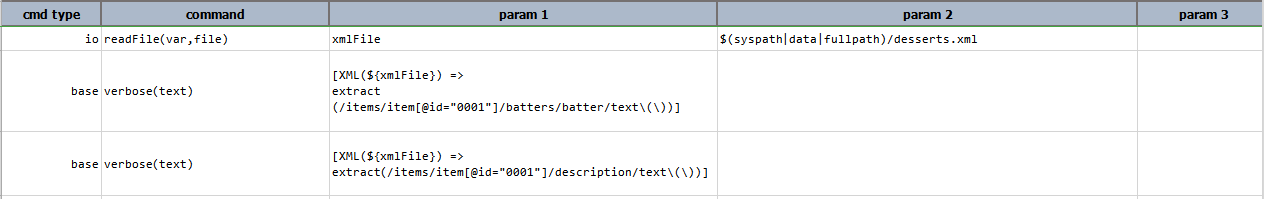
Output:

insertAfter(xpath,content)
Search against specified xml via xpath, and insert content after all matching instances.
Example
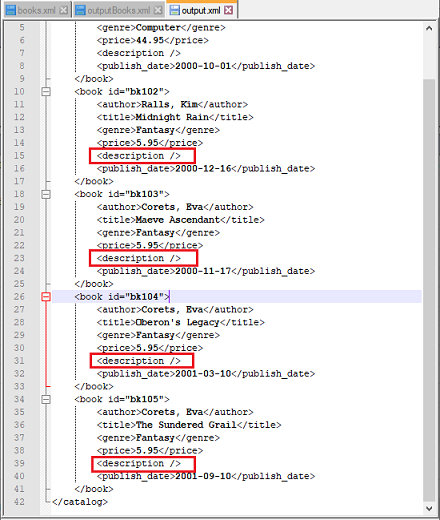
Input XML file: books.xml

Script: Insert new tag description after publish_date.

Output File:

insertBefore(xpath,content)
Search against specified xml via xpath, and insert content before all matching instances.
Example
Input XML file: books.xml

Script: Insert new tag description before publish_date.

Output File:
minify
Compressed current XML document which are suitable for effecient data transfer.
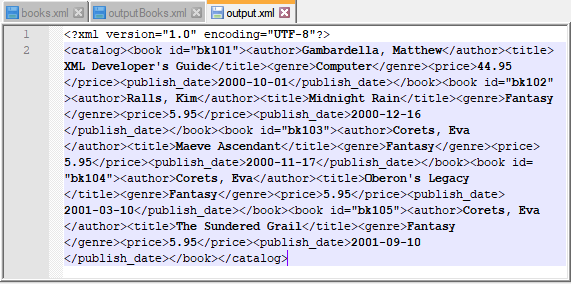
Example
Input XML file: books.xml

Script: Minify the above XML.

Output File:
prepend(xpath,content)
Search against specified xml via xpath, and prepend content to all matching instances.
Example
Input XML file: bookstore.xml

Script: Prepend the string "publishing year = " to each publish_year.

Output File:

remove(xpath)
Remove from the source XML the element(s) that matches the specified xpath. This operation is the same as
delete(xpath).
Example
Input XML file: bookstore.xml

Script: Remove author from each book in Web category.

Output File:

replace(xpath,content)
Search against specified xml via xpath, and replace content against all matching instances. This command
is different from replaceIn(xpath,content) in that it replaces the tags as well as the
content of the matching elements while replaceIn(xpath,content) only replaces the content
of the matching elements.
Example
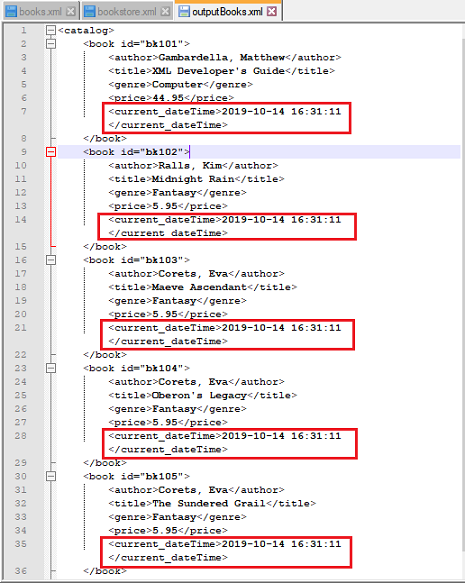
Input XML file: books.xml

Script: Replace the publish_date in each node with current_dateTime containing the current date and time.

Output File: As seen below, the entire line containing the publish_date tag along with its content was
replaced by the current_dateTime tag and its content.
replaceIn(xpath,content)
Search against specified xml via xpath, and replace inside content of all matching instances. This command
is different from replace(xpath,content) in that it only replaces the content of the
matching elements while replace(xpath,content) replaces the tags as well as the content
of the matching elements.
Example
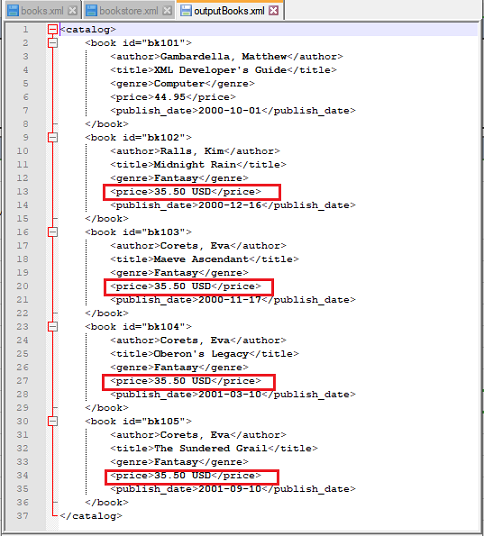
Input XML file: books.xml

Script: Replace the price of each book in the Fantasy genre with 35.50 USD.

Output: As seen below. only the content of the price tag was replaced, the tag itself remains unmodified.
Note: replaceIn(xpath,content) and updateContent(xpath,content) are the same when
the specified xpath points to an XML node.
save(path,append)
Save current expression content to path. If path resolves to an existing file, append set as true will append
current expression content to the said file. append is optional and defaults to false.
Example
Input XML file: books.xml

Script: Save all the books published in the year 2000 to another XML.
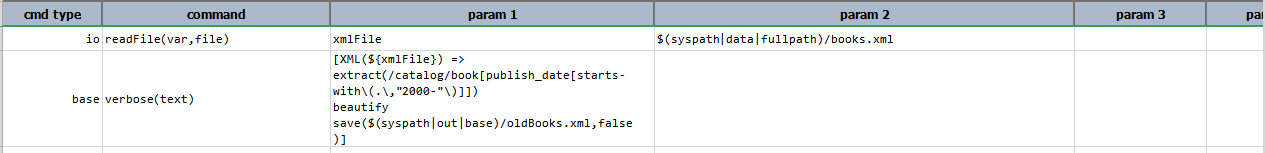
Output File:
store(var)
Save current XML expression to a data variable. If the specified var exists, its value will be overwritten. Using
this operation, one can put an expression on pause and resume it at a later time.
Example
Input XML file: bookstore.xml

Script: newXml contains the expression to extract all the books from the year 2005. We then use this variable to
extract the books belonging to the Cooking category.
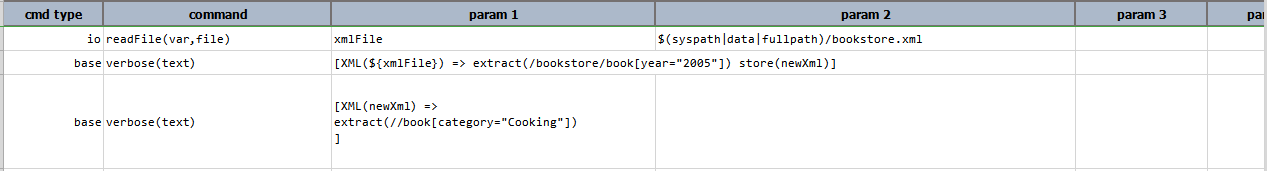
Output:
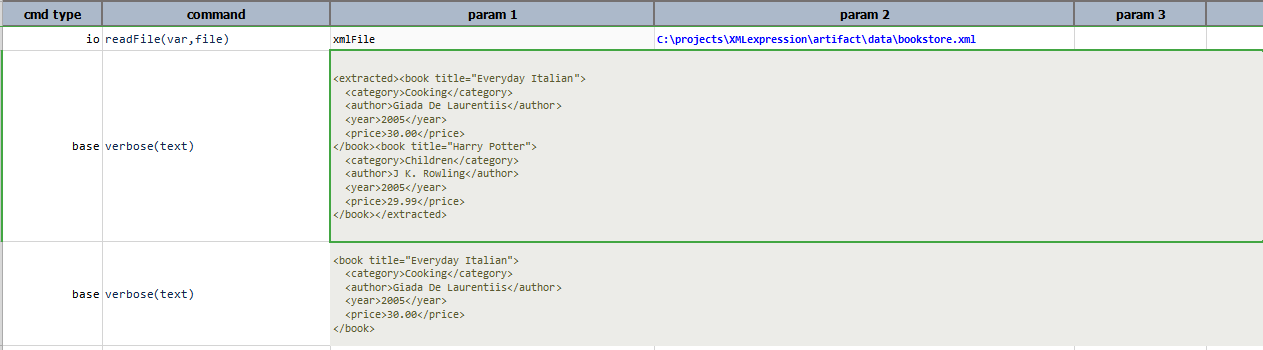
text
Transform current XML document into its textual representation.
Example
Input XML file: bookstore.xml

Script: Transform above XML to text.

Output File:
updateAttribute(xpath,name,value)
Also known as update-attribute(xpath,name,value). This operation updates the attribute of all matched elements
based on name and value. If value is empty, then the target attributes are effectively removed.
Example
Input XML file: bookstore.xml

Script: Update the title of every book to new Title.

Output File:

updateContent(xpath,content)
Also known as update-content(xpath,content). This operation updates (technically speaking, replace) the content
of the matched elements with the specified content. content may be text or XML nodes. If content is empty, then
the content of the target elements are effectively removed.
Example
Input XML file: bookstore.xml

Script: Update the price of each book from the year 2005 to 50.00.

Output File:

Note: updateContent(xpath,content) and replaceIn(xpath,content) are the same when the
specified xpath points to a XML node.