System Variables
Nexial comes with a set of configuration parameters that control or affect test execution. These configuration
parameters can be specified the same way as test data. Many of them can be independently created per iteration
(except those starting with nexial.scope.). Many of them can also be specified via command line
argument (i.e. via -D option), which will override the same settings in data file.
Nexial is written predominantly in Java. User can configure the JVM memory allocation (the amount of memory usable
by the Java process that executes Nexial) via the NEXIAL_MAX_MEM environment variable. To
specify this environment variable:
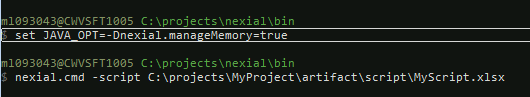
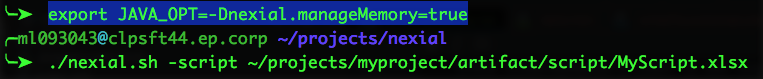
On Windows, before running nexial.cmd:
set NEXIAL_MAX_MEM=4096m
On Linux/Mac OS, before running nexial.sh:
export NEXIAL_MAX_MEM=4096m
The above specifies for 4GB of memory for Nexial.
For more details about the exit status that Nexial emits at the end of execution, or a set of standard output at the end of execution, please click on the links below.
It is good to be aware that Nexial comes with a set "special" handling for certain non-printable characters. One may use these within the scripts in order to render characters not easily recognized on a spreadsheet:
(eol) - this represents the newline (carriage return or line feed) character(empty) - this represents no input. Rather than leaving a parameter empty, one can use this to
clarity the input intent
(blank) - this represents 1 space. Since it is hard to see spaces in a spreadsheet, one might opt
for using this for clarity's sake
(tab) - this represents 1 tab character. Again, use this to improve readability.(null) - this represents the null character, which is rarely needed. Some commands
might have specific use for such representation.
Below are a list of configurable system variables. During the test execution, Nexial may generate one or more variables which maybe incorporated as part of your test script.
For standard System properties, see the section below titled as Standard System Properties.
| configuration | data type | default | read only? | description | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
nexial.executionType |
text | read-only |
Read Only System variable to indicate the type of execution currently in progress. The only possible values
are:
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.runID |
text | read-only |
The unique identifier for each test execution, derived at the beginning of the execution. Generally this is
the start of execution in the form of yyyyMMdd_HHmmss.
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.runID.prefix |
text | read-only |
Optional prefix to the system-generated nexial.runID, which is based on the timestamp of the
start of an execution. This will directly impact the output directory, in that both the prefix and the
autogenerated runID will represent the output directory name.The purpose of using a prefix has manifolds. Read on... Organize your output better Surely you can see how this: 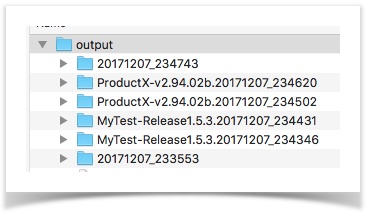 ... is more organized and informative than: 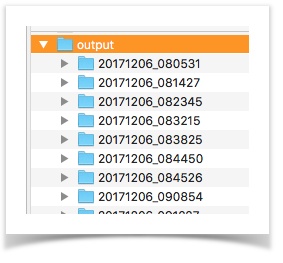 Create dashboard of your executions Using the same prefix, we can collect a series of execution to be summarized together. For example, 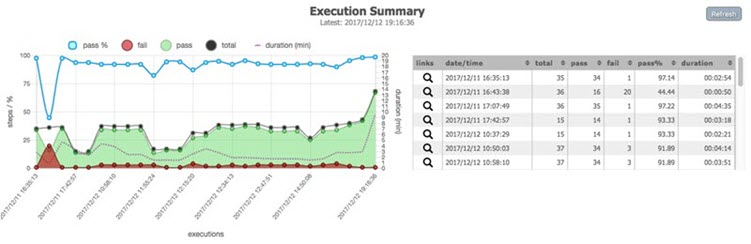 Using the above summary, one can track the change in execution over time - total steps, pass % and execution duration. NOTE: this System variable MUST be specified during execution. Specifying it in a data file will have no effect. Below are a couple of examples: set JAVA_OPT=-Dnexial.runID.prefix=Sprint14 -Dnexial.outputToCloud=true
nexial.cmd -plan ...
nexial.cmd -script ...
-override nexial.runID.prefix=Sprint14
-override nexial.outputToCloud=true
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.env |
text | read/write |
MUST BE SET FROM COMMAND LINE VIA -override or set JAVA_OPT=-D...This System variable instructs Nexial to load an environment-specific project.properties AFTER
loading the default artifact/project.properties file. For more details and examples, see the
Through project.properties page.
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.projectProperties.trimKey
|
boolean | false | read/write |
MUST BE SET FROM COMMAND LINE VIA -override or set JAVA_OPT=-D...This System variable instructs Nexial to load the project.properties with the data variable
names (i.e. the property keys) trimmed. As such the data variable name derived from the
project.properties will not contain any leading or trailing whitespaces.One can consider this System variable as a form of improving readability over project artifacts. Consider the following 2 project.properties:
 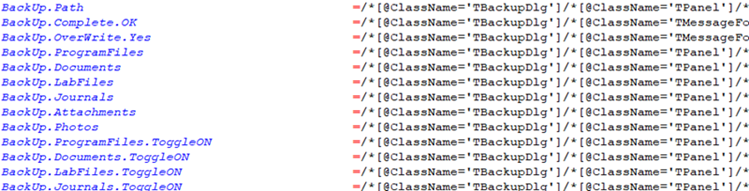 One may argue that the latter looks more organized. Many of the modern text editors support this sort of text formatting. If one would like to structure the project.properties so that the data
variable values aligned (shown above as the latter image), then set this System properties as true. However,
note that this System variable MUST BE SET FROM COMMAND LINE via the -override parameter
or via the set JAVA_OPT=-D... environment variable.By default, this System variable is set to false for backward compatibility.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.projectPropertiesDups
|
text | error | read |
MUST BE SET FROM COMMAND LINE VIA -override or set JAVA_OPT=-D...This System variable instructs Nexial how to handle the situation when duplicate data variable is found in project.properties. Here are the options:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.verbose |
boolean | false | read/write | Determine if additional log information should be captured in the output. The additional log information differs from command to command, and will be displayed in the subsequent row (i.e. below the test step). | ||||||||||||
nexial.quiet |
boolean | false | read/write |
A.K.A. the quiet mode. Set this System variable to true to drastically reduce the amount of console logging during
execution. Most notably, the PASS or FAIL logs will be omitted when
quiet mode is enabled. The
base » verbose(text) will still be logged
to console, along with start of each step. However, log file (stored to $(syspath|log|fullpath))
will not be affected by this System variable.The quiet mode only affects console logging, and is most useful when the reduction of such ease one's attempt to follow the execution flow. |
||||||||||||
nexial.elapsedTimeSLA |
millisecond | read/write |
Determine the elapsed time of any test step to be considered as out of compliance (outside of SLA). Such
test step would be marked as FAIL with
explanation in the result column.Note that this SLA will not be applicable to the composite commands such as:
Similarly, all the wait... commands will be exempt from this SLA check since such command would
likely contain its own SLA (aka timeout) enforcement.
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.lastElapsedTime |
millisecond | read-only | Represent the elapsed time in millisecond of the last executed step (regardless of its PASS or FAIL status). | |||||||||||||
nexial.delayBetweenStepsMs
|
millisecond | 600 | read/write | The wait time between test steps, in milliseconds. | ||||||||||||
nexial.textDelim |
text | , |
read/write |
The delimiter character to split a string of characters into array. For example, Apple,Banana,Orange would be split into an array of 3 elements:
Apple, Banana and Orange. However, using the default comma might not always be the best option. Overriding this configuration provides the flexibility needed to transform a single text string into an array of text. |
||||||||||||
nexial.resolveTextAsURL |
boolean | false | read/write |
When set to true, this System variable instructs Nexial to make the attempt of resolving the
text parameter of a command or expression - where appropriate - as a valid URL. If such resolution is
attained, Nexial automatically substitute such text parameter with the content behind such URL (HTTP GET).
This can simplify the automation tasks at hand, esp. when there are multiple URL-backed content, or if the URL is dynamically generated. By default, this System variable is set to false to avoid any
undesired surprises.Currently this System variable, and the underlying feature, is applied to TEXT Expression and ws commands, with other areas of Nexial soon to follow.Note that this System variable supersede the now-deprecated nexial.expression.resolveURL System variable.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.resolveTextAsIs |
boolean | false | read/write |
When a parameter points to a local file (fully qualified path), Nexial will by default performs the
following:
The above is the default behavior, and most likely the desired behavior However, at times one might want to avoid such automation (i.e. data variable substitution). To disable Step #2 (data variable substitution), one would set the value of this System variable to true.
Note that this System variable supersedes the now-deprecated
nexial.expression.OpenFileAsIs System variable.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.nullValue |
text | (null) |
read/write |
Change the default representation of a null value. Leaving a cell empty can be confusing - is it
null, empty, blank? To improve readability and maintainability, Nexial uses the following as reserved word:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.var.ignored |
text / list | read/write |
By default Nexial searches for data variables in the form of ${...} and substitutes them with
the corresponding value. This is a useful feature to create dynamic data substitution and generation.However at times it is important that some data variables are left as it is. It might be a case of multi- stage text processing where Nexial is used to process some data variables and another program for additional data variables (which should be left alone). It might be a case of time-triggered processing where some data variables become available/meaningful at a later time (and thus should be ignored presently). Whatever the case may be, one can use this System variable to define a list of data variables to be ignored. All the data variables defined in this System variable will be left as is. It is important to note that this System variable should be ONLY the data variable name. For example, the following is considered correct: 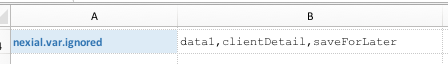 But the following is considered incorrect: 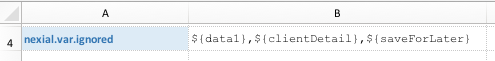 |
|||||||||||||
nexial.var.defaultAsIs
|
boolean | false | read/write |
By default Nexial searches for data variables in the form of ${...} and substitutes them with
the corresponding value. If a data variable, as derived from the ${...} syntax, is not found
or is not associated with a value, Nexial will replace the corresponding ${...} with empty
value - effectively removing that ${...} text.However at times it may be important NOT to substitute missing data variable with empty value and keep the ${...} as is. Perhaps the missing data variable(s) will be made available later in
the execution or be handled by another downstream process. For this reason, one can use this System variable
to instruct Nexial NOT to empty out non-existing data variable substitution.By default, this System variable is set to false. Changing it to true will leave
all non-matching ${...} as is.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.outputToCloud |
boolean | true | read/write |
Determine if execution output (report, screenshots, etc.) should be saved to cloud storage so that they may
be retrieved remotely. When such configuration is turned on, the console log will indicate as such: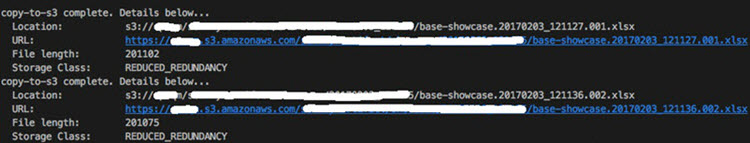 Follow this guide for one-time setup of nexial.outputToCloud configurations.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.subplansIncluded
|
text | read-only |
This variable provides all worksheets/subplans executed while running specific
-subplans command option during Single plan
execution.
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.subplansOmitted |
text | read-only |
This variable provides all worksheets/subplans omitted while executing specific
-subplans command option during Single plan
execution.
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.scriptRef.* |
text | read/write |
This configuration does not modify the behavior or outcome of a test execution. Instead, it is used to
create reference information, which may change over iteration, to improve the readability of the execution
output. For example,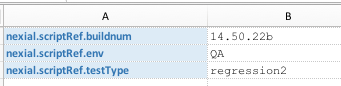 Adding these information - while one may reference them within script - do not necessarily change the execution or behavior of related script(s). However, the output would look something like this: 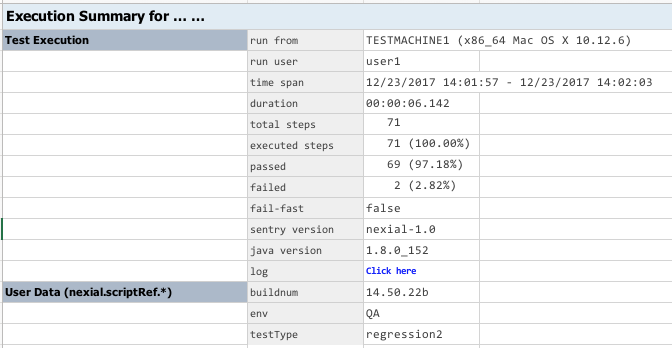 As such, the output provides contextual information about the execution such as:
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.scenarioRef.* |
text | read/write |
This configuration has a similar purpose as that of nexial.scriptRef.*, except it applies
to the scenario level (not script). As such, one can provide context information at the scenario level,
which can
possible change over iterations. Example: Here the companyId is changing from 15 to 1602 between iteration 1
and 2.
The output would reflect as such: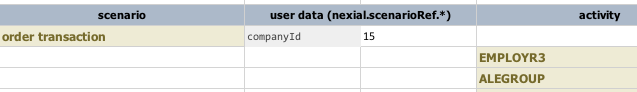 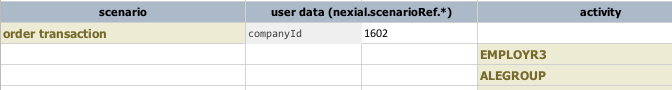
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.stepByStep |
boolean | false | read/write |
Determine if Nexial to pause after each test step. When set to true, Nexial will pause test execution after
each step. User will need to press Enter on the console to resume the next step.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.inspectOnPause |
boolean | false | read/write | During PauseBefore() or PauseAfter(), it is possible to interact with Nexial to inquire of the state of a data variable, a built-in function or a Nexial expression. For more details, visit this page. | ||||||||||||
nexial.pauseOnError |
boolean | false | read/write |
During script development, it is often advantageous to "step through" the execution so that improvements
and correction can be made upon runtime observation. However, for a very large execution run, it might be
rather time-consuming to re-run the execution from the beginning each time. Having a way to course correct
when a FAIL condition is encountered during execution could be very helpful. This is the premise of this System variable. When set to true, Nexial will pause the execution
when a FAIL condition is encountered. This gives automation engineer an opportunity to observe and trace
through both the AUT and the script in action. When use in combination with
nexial.inspectOnPause, this can be an even more powerful
tool to work through the FAIL condition as and when error occurs.By default, this System variable is set to false.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.odiEnabled |
boolean | true | read/write |
Enable (default) or disable
On-Demand Inspection (ODI).
Turning off ODI has the benefit of slightly faster execution. However, its benefits often outweighs the cost thereof. During active script development or troubleshooting, it is usually recommend to leave this feature enabled. Like most interactive feature, ODI is disabled - by design - when Nexial is executing in the CI/CD environment. |
||||||||||||
nexial.odiTimer |
millisecond | 500 | read/write |
Determine the frequency, in milliseconds, of input detection by the On-Demand Inspection (ODI) "listener".
Note that setting this value too low could cause an execution to hang or become unresponsive since there
could be too much resource contention between the main execution thread and the "listener" thread. The
minimum allowed value is `300` (ms); the default is `500` (ms). See On-Demand Inspection (ODI) for more details. |
||||||||||||
nexial.odiKeys |
text | !!! |
read/write |
Determine the key sequence to activate On-Demand Inspection. The default value is !!! but one
can change it to other ASCII character sequence. Note that compound key sequences that contains
[CONTROL], [ALT], [WIN], [OPTION] and
[COMMAND] are not supported, as such are usually trapped by the underlying console
application.See On-Demand Inspection (ODI) for more details. |
||||||||||||
nexial.failFast |
boolean | false | read/write | Determine how Nexial should handle the test execution when a failure is found. Failure could either be an unexpected outcome of an action, or the undesired result of a validation. If set to true, Nexial will terminate the test execution after the first occurrence of a failure. Otherwise, Nexial will continue to the subsequent test step. In either case, failure will be reported accordingly. | ||||||||||||
nexial.resetFailFast |
boolean | false | read/write |
Determine if the failure condition of one script should cascade down to subsequent scripts. Only applicable
when using test plan. The typical use case for using such system variable would be something such as:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.failImmediate |
boolean | false | read/write |
Determine if Nexial should terminate execution at the next failure. This configuration can be useful to
signify the intent of "after this point, failure will not be tolerated". For example,
|
||||||||||||
nexial.disableCriticalCommands |
boolean | false | read/write |
Determine if Nexial should consider the failure of "critical" commands as a condition for "fail immediate".
Critical commands are considered to be of utmost importance that no automation should tolerate such
corresponding failure. This means that failure on the execution of one of these critical commands will
trigger a "fail immediate" condition and the execution will promptly terminate. In other words, the
continuing of the execution after a failure to one of these critical commands is not likely useful or
meaningful. As this time, here are the list of critical commands: However, at times it is important (or, more "critical") that we don't terminate execution on account of such failure condition. One such example is the testing or the simulation of network outage or resource failure. In order to support such execution goals, one can use this System variable - nexial.disableCriticalCommands - to temporarily disable to triggering of "fail immediate"
condition. Setting this System variable to true will disable such triggering.By default, this System variable is set to false (hence the failure of critical commands will
trigger "fail immediate" condition. |
||||||||||||
nexial.maxConsoleDisplay
|
integer | 500 | read/write |
In cases where a data variable might hold a large amount of text, it might not always be the best idea to
display its entirety on the console. Lengthy console output might make the rest of the execution log
more difficult to read, as well as slowing down the execution a bit. For these reasons, this System variable is designed to cut down the display of the data variable with large amount of data. By default, this System variable is set to 500. This means that only the first 500 characters (up to) will be displayed on the console. One may choose to modify this System variable to fit one's need. To disable limiting the number of characters to display, set this System variable to -1.This System variable currently impacts only the following commands (but will be expanded to more soon):
Note that this will have no effect on the actual content of the data variable. |
||||||||||||
nexial.printErrorDetails
|
boolean | false | read/write |
When set to true, Nexial will print out additional details (i.e. exception stack trace) when
an error occurred while processing a command. Not usually needed, but could be useful during
troubleshooting or root cause analysis.By default, this System variable is set to false
|
||||||||||||
nexial.lastError
|
text | read-only | This System variable stores the last FAIL message. | |||||||||||||
nexial.trackErrors
|
boolean | false | read-write |
Setting this System variable to true would activate
ErrorTracker, where each of the
failed steps of an execution would be tracked to a logs/nexial-execution-errors.log file. This
can greatly improve the process of root cause analysis or postmortem discovery since only errors and failed
steps
are "trapped" in this designated file.This feature is disabled by default (i.e. false).
|
||||||||||||
nexial.targetDisplay
|
integer | 0 | read/write |
Set this System variable to the corresponding target display (i.e. computer monitor) where the AUT should be
rendered. Note that this is a 0-based System variable, and by default is set to 0.
Setting this System variable to, say, 1, instructs Nexial to render the AUT (most likely
the web browser) in the 2nd monitor. Please consult with the display setting of the compute resource that is
executing Nexial Automation. This System variable is useful when one intends to display the automation in
action on a specific display output (such as during triage, demo, joint sessions).
One can use a special keyword - CURRENT - to instruct Nexial to open the AUT in the display
currently in focus. Hence, from the same display (monitor) where Nexial is executed, the AUT will be displayed
on the same display as well.
Note that changing this System variable will also have implication to the following:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.screenshotEnabled
|
boolean | true | read/write |
Only applicable to web, desktop commands.Set this System variable to false to disable all screen capturing during execution. When this
System variable is set to false, the following commands will render SKIP as
outcome:
By default, this System variable is set to true.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.screenshotOnError
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Only applicable to web, desktop commands.Set to true for Nexial to capture screenshot when a failure occurred.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.screenshotAsDesktop
|
boolean | false | read/write |
When running web commands, the norm has been using the underlying
WebDriver's screen capturing capability. However, in some situation, it might be beneficial or perhaps
necessary to screen capture the entire "desktop" instead. For one, WebDriver's screen capture will not be
able to capture any native desktop rendering, such as a "file chooser" dialog often seen during a file
upload process: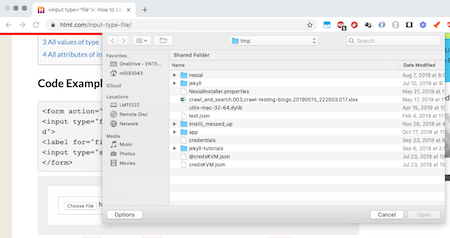 By setting this System variable as true (default is false), Nexial will capture
the entire desktop instead of what the browser renders. Note that desktop screen capturing usually
only capture the primary screen (a.k.a. Screen 1).
|
||||||||||||
nexial.screenshotInFull
|
boolean | false | read/write |
When running web commands, the norm has been using the underlying
WebDriver's screen capturing capability. However, in some situation, it might be beneficial or perhaps
necessary to screen capture the entire web page instead. By setting this System variable as true (default is false), Nexial will capture
the entire web page instead of what the browser renders.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.screenshotInFullTimeout
|
integer | 5000 | read/write |
When running web commands, the norm has been using the underlying
WebDriver's screen capturing capability. However, in some situation, it might be beneficial or perhaps
necessary to screen capture the entire web page instead. So, while capturing full screenshot, the timeout
needed to
load image before scrolling to next screen is specified via this variable. Default value is
5000
(in milliseconds). This system variable only comes in effect if
base » index#nexial.screenshotInFull is set
to true
|
||||||||||||
nexial.screenshot.caption
|
text | read/write |
Optional caption for each captured screenshot. When performing desktop or web automation, one can indicate the desire to capture the screenshot (of the current active desktop or application) after completing a specific test step. This is done by marking a x on the corresponding test step (at Column L).However, one might find it useful to "annotate" the screenshots with additional text to provide further clarity or context. For example, compare the following 2 captured screenshots:   These two images are practically identical, except the second one has additional caption at its bottom-right corner. As such, the second image provides its viewer information that may be helpful towards understanding its context or troubleshoot an underlying defect. To generate caption, simply define the caption to use via this System variable. For example:  Notice that Nexial built-in functions are used here. One can use regular data variable, built-in functions and Nexial expression dynamically define the screen captions. Note that, while it is possible to specify this System variable via base » base(var,value) command, it is not
recommend because the caption will be evaluated and saved as is when the corresponding test step is
executed. Instead, define this System variable via a data file or project.properties to
maintain its dynamic value (geek term: late binding).See other nexial.screenshot.caption.* System variables for more configuration options.
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.screenshot.caption.color
|
text | yellow | read/write |
NOTE: nexial.screenshot.caption MUST BE SET TO
true IN ORDER TO ACTIVATE THIS FEATURE.Determine the caption color to use. Choose one of the predefined colors list below:
nexial.screenshot.caption.noBackground
System variable.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.screenshot.caption.alpha
|
decimal | 1.0 | read/write |
NOTE: nexial.screenshot.caption MUST BE SET TO
true IN ORDER TO ACTIVATE THIS FEATURE.Determine the transparency level of the caption to render. The default is 1.0, which means
"zero transparency". It is usually not recommended to change this System variable since textual transparency
might affect the readability thereof. In certain situation, such as white text on very dark images, it
might be reasonable to turn on some transparency (i.e. 0.8 for 20%).
|
||||||||||||
nexial.screenshot.caption.noBackground
|
boolean | false | read/write |
NOTE: nexial.screenshot.caption MUST BE SET TO
true IN ORDER TO ACTIVATE THIS FEATURE.Determine if Nexial should generate the caption with a background color that is "complimentary" to the selected text color. Default is false, which means that Nexial will generate the caption with
a complimentary background color.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.screenshot.caption.position
|
text | bottom,right |
read/write |
NOTE: nexial.screenshot.caption MUST BE SET TO
true IN ORDER TO ACTIVATE THIS FEATURE.Determine the position of the caption using one of the following positions:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.screenshot.caption.wrap
|
boolean | false | read/write |
NOTE: nexial.screenshot.caption MUST BE SET TO
true IN ORDER TO ACTIVATE THIS FEATURE.If set to true the caption text will be rendered as one contiguous line. This means that
any extraneous leading or training spaces, tabs, carriage returns and newline characters will be removed.
If set tofalse (default), then the caption will be kept as is.In either case, the caption will be rendered with text wrapping enabled as needed. See nexial.screenshot.caption for more details. |
||||||||||||
nexial.lastScreenshot |
text | read-only |
The fully qualified path of the last screenshot taken (meaning that the "screenshot" column in the test
script is marked with x). If
nexial.outputToCloud is set to true, this
System variable will return the equivalent URL instead.
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.lastOutcome |
boolean | read-only |
A true or false to indicate the outcome of the last command. This can be useful
when used as flow control condition. For example, Since myNumber is not 6, the assertion (2nd line) will fail. Now using the
${nexial.lastOutcome} as the condition, we can fail the entire execution when a
critical error is found.
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.lastPlanStep |
boolean | false | read/write |
A true or false, indicate to stop or continue the execution after the script.
This can be useful when one wants to interrupt/stop execution flow immediate after completion of the script.
This would be last step in the plan executions. This is only applicable while running a plan as only plan
will have multiple scripts. It should be set in respective data file of the script.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.lastOutputLink |
text | read-only |
This system variable reflects the filename of the output generated via certain commands, such as:
${nexial.outputToCloud} is set to true) -
will be made available via this System variable as well. This may further enhance one's automation
experience since one could utilize the same output link as part of the execution.
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.lastOutputPath |
text | read-only |
This system variable reflects the location of the output generated via certain commands, such as:
${nexial.outputToCloud} is set to true) -
will be made available via this System variable as well. This System variable has the same value as
nexial.lastOutputLink - BUT WITHOUT THE FILE NAME. This
may further enhance one's automation experience since one could utilize the same output path as part of the
execution.
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.failAfter |
integer | read/write |
Determine the number of failure that can be tolerated before Nexial forcefully terminates the test
execution. In effect, this System variable provides a way to implement a "fail-not-so-fast" execution.
nexial.failFast (when set to true) provides a way to terminate execution on the
first occurrence of a FAIL condition (of a command) - hence "fail-fast". In contrast, the
nexial.failAfter System variable "slows down" the execution termination by allowing for FAIL
conditions to occur. By specifying an integer value to nexial.failAfter, one can apply the idea
of "error tolerance" to prolong an execution that contains failures. A sort of failure-grace, as it
were.
Note that this System variable supersedes nexial.failFast, and FAIL count is not reset across
scripts, iterations or scenarios. By default, this System variable is not activated.
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.minExecSuccessRate
|
decimal | 100 | read-only |
By default, only an execution with 100% PASS rate would be considered as a SUCCESS. Well, from time
to time, success isn't always that straightforward. There might be valid and one-off reason as to why the
criteria of SUCCESS would be more lenient. Using this system property, one can tune the minimum rate of
PASS(es) in order for an execution to be considered as SUCCESS. An SUCCESS will in turn yield a
exit status of 0, which is the equivalent in scripting of
"everything's fine, proceed on!". This can be very useful (and indeed necessary) for CI/CD
environment, or when a Nexial execution is part of a bigger scripting effort.By default, this system variable has a value of 100 (as in 100%). Specifying a number lower
than 100, such as 95.51 to fine tune the criteria for a SUCCESSful execution.
Mis-configured value (less than 0 or greater than 100) will be ignored.NOTE: this system variable is NOT read from data file, and MUST be specified via command line. For example, nexial.cmd -plan ...
-override nexial.minExecSuccessRate=97.55
-override nexial.openResult=true
At the end of an execution, one may observe a printout of the SUCCESS evaluation due to this system
variable. For example,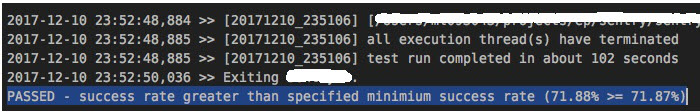
See Exit Codes and End of Execution for more details about this topic. |
||||||||||||
nexial.executionCount
|
integer | read-only | The number of steps executed at the time of this System variable being referenced. Note that this represents the cumulative total number of steps executed within one execution, which span across the plans, scripts, iterations, scenarios and activities of the same execution. | |||||||||||||
nexial.executionPassCount
|
integer | read-only | The number of PASS steps at the time of this System variable being referenced. Note that this represents the cumulative total number of PASS steps within one execution, which span across the plans, scripts, iterations, scenarios and activities of the same execution. | |||||||||||||
nexial.executionFailCount
|
integer | read-only | The number of FAIL steps executed at the time of this System variable being referenced. Note that this represents the cumulative total number of FAIL steps within one execution, which could span across the plans, scripts, iterations, scenarios and activities of the same execution. | |||||||||||||
nexial.executionSkipCount
|
integer | read-only | The number of steps skipped (not executed) at the time of this System variable being referenced. Note that this represents the cumulative total number of steps skipped within one execution, which span across the plans, scripts, iterations, scenarios and activities of the same execution. | |||||||||||||
nexial.currentActivity
|
text | read-only | This system variable is to indicate the Activity currently in Execution. It will only show activity name currently executing. | |||||||||||||
nexial.currentScenario
|
text | read-only | This system variable is to indicate the Scenario currently in Execution. It will only show scenario name currently executing. | |||||||||||||
nexial.summary.header
|
text | read-only |
Allow one to customize "header" content in the execution summary generated at the end of a Nexial execution.
One could define this System variable like the following:  The generated execution summary would now contain the customized "header": 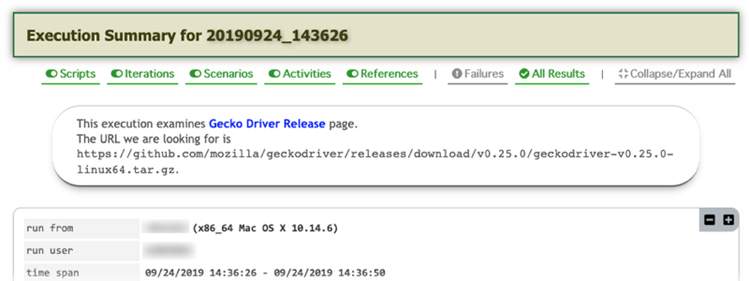 |
|||||||||||||
nexial.summary.footer
|
text | read-only |
Allow one to customize "footer" content in the execution summary generated at the end of a Nexial execution.
One could define this System variable like the following:  The generated execution summary would now contain the customized "footer": 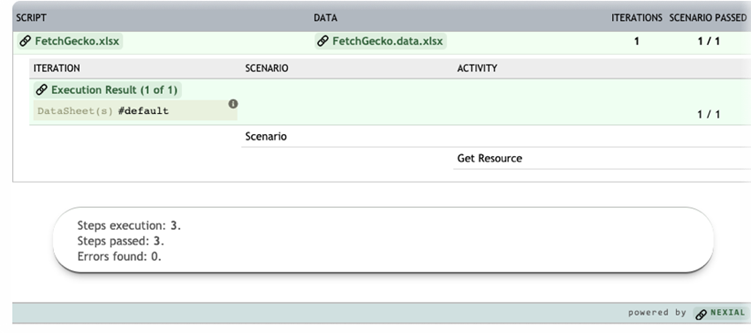 |
|||||||||||||
nexial.manageMemory |
boolean | false | read-only |
MUST BE SET FROM COMMAND LINE VIA -override or set JAVA_OPT=-D...To turn on this variable, one must set the -D environment variable prior to executing a test
run. For example:
[on Windows]: nexial.manageMemory=true), Nexial will conduct garbage collection (GC) to reclaim any
unused heap memory after the completion of each test script execution. You will see something similar as
the following, which show that GC was executed and the memory footprint changes between the GC. At the end of the entire execution, Nexial also print out a summary of the memory usage between different test scenarios: 
|
||||||||||||
nexial.assistantMode |
boolean | false | read/write |
DEPRECATED SYSTEM VARIABLE NAME.
PLEASE SEE nexial.openResult INSTEAD.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.openResult |
boolean | false | read/write |
Determine if Nexial should automatically open the output in Excel after each iteration. This could be a
time saver since one would not have to manually search for the output file. This configuration is forcefully turned off during remote execution. |
||||||||||||
nexial.spreadsheet.program
|
text | excel | read-only |
Configure the full path, including the executable name, of the program to use when opening Nexial output at
the end of an execution run. This is only applicable when nexial.openResult is enabled. By
default, Nexial will invoke Microsoft Excel to open the execution output in context.However, should you choose to use another program, such as WPS, specify this variable in your data sheet. For example,  Alternatively, one can simply specify wps, which will enable Nexial to automatically resolve
the correct location of WPS (the latest version preferred). For example,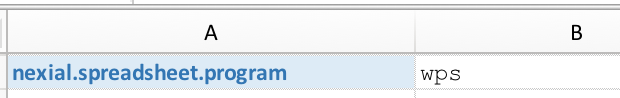
|
||||||||||||
nexial.generateReport
|
boolean | true | read/write |
This System variable instructs Nexial whether to generate the JSON-based report or not. The JSON reports
(2 JSON files, to be exact) are useful towards the execution summary report and TMS integration (Test
Management Systems, like JIRA or TestRail). One could set this System variable to false to omit
the JSON file generation if neither execution summary nor TMS integration is of interest.This System variable is set true by default, meaning that the JSON reports will be generated at the end of each execution. |
||||||||||||
nexial.step.response
|
text | read/write |
The commands in step and
step.inTime are designed for automation where human
interaction
(or intervention) is needed. As such, these commands prompt for user input in the form of a "response"
and/or
"comment".This System variable captures the "response" provided by the user during the execution of such command. One may include the content of this System variable as part of the automation. For example, the "response" can be included in an email generation or an output file. |
|||||||||||||
nexial.step.comment
|
text | read/write |
The commands in step and
step.inTime are designed for automation where human
interaction
(or intervention) is needed. As such, these commands prompt for user input in the form of a "response"
and/or
"comment".This System variable captures the "comment" provided by the user during the execution of such command. One may include the content of this System variable as part of the automation. For example, the "comment" can be included in an email generation or an output file. |
|||||||||||||
| For text-based assertion only. | ||||||||||||||||
nexial.assert.lenient
|
boolean | true | read/write | Determine if string comparison should be "forgiving" by converting newline and carriage return characters to space BEFORE comparison starts. This is generally needed for Internet Explorer based automation. It is usually safe to leave this at default value. | ||||||||||||
nexial.assert.asNumber
|
boolean | true | read/write |
Perform text assertion by first converting both the expected and actual text to number - if they are in fact
numbers. As such, 1 would be treated the same as 1.0.Note that setting this System variable to true (default) does not render any text into a
number.
Only those of valid numeric form (decimals ok) will be converted into numbers.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.assert.useTrim
|
boolean | read/write |
Perform text assertion by first trimming (both leading and trailing) spaces from text. Default is
false (no trimming).
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.assert.caseInsensitive
|
boolean | read/write |
Perform text assertion case-insensitively. Default is false.
|
|||||||||||||
| For screen recording only. | ||||||||||||||||
nexial.recordingEnabled
|
boolean | true | read/write |
Determine if the screen recording is enabled or not during test Execution. This system variable
CAN be read from data file, specified via command line or via
project.properties.
This can be useful when toggling between environments where screen recording is not ideal (such as
CI/CD).NOTE: by default if no system variable defined, recording is set to true (enabled) by default |
||||||||||||
nexial.recordingAutostart
|
text | none | read/write |
This System variable instructs Nexial to automatically start desktop recording (on primary monitor) when
a specific event occurs. This can be greatly simplify one's automation script by eliminating the explicit
invocation of base » startRecording and
base » stopRecording.Currently the only event supported is execution. By assigning execution to this
System variable, Nexial will automatically start the desktop recording at the execution of the first command.
Future releases of Nexial will support automatic screen recording based on other events such as:
cd $NEXIAL_HOME cd bin nexial.cmd -script C:\projects\X\artifact\script\Y.xlsx -override nexial.recordingAutostart=executionBy default, this System variable is assigned the value none.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.screenRecorder |
text | mp4 | read-only |
Determine format of the recording file need to be created. Currently supported screen recording files to be
mp4 (default) or avi |
||||||||||||
| For number-related functionality. | ||||||||||||||||
nexial.number.rounding
|
text | ROUND_UP | read/write |
Customize how one would like the decimal rounding logic to be implemented. This System variable only impacts
the following functionality:
This System variable can be configured as one of the following:
|
||||||||||||
| For email notification only. | ||||||||||||||||
nexial.enableEmail |
boolean | false | read/write |
Enable email notification at the end of an execution. By default, this is not enabled as using email to
communicate execution status carries a variety of possible side issues. Nonetheless, email notification is
supported in Nexial. Such email provides summary information for a given execution, and it looks like the
following: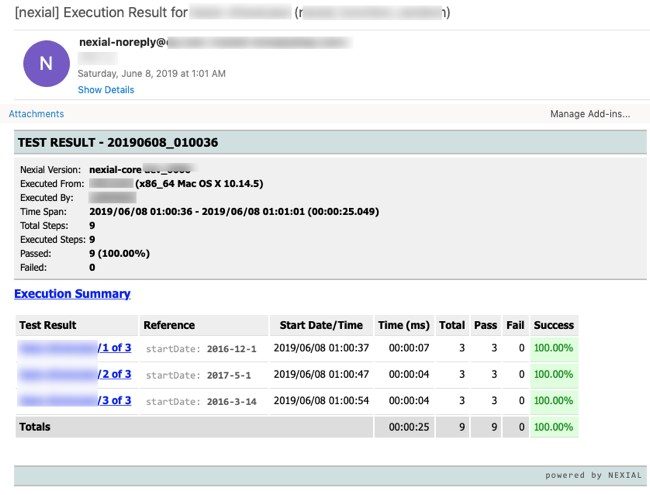 Note that the "Reference" column reflects the nexial.scriptRef.*
values defined for each script/iteration.Here are the steps:
JAVA_OPT=-D... or -override
flag),
project.properties
or the appropriate data file. For example, from command line:nexial.sh -script ... ... \
-override nexial.enableEmail=true \
-override nexial.mail.smtp.host=mail.mycompany.com \
-override nexial.mail.smtp.auth=false \
-override nexial.mailTo=me_and_myself@mycompany.com
|
||||||||||||
nexial.mailTo |
text | read/write |
NOTE: nexial.enableEmail MUST BE SET TO
true IN ORDER TO ACTIVATE THIS FEATURE.A comma-separated list of email addresses to receive Nexial's email notification at the end of an execution. Note that this System variable, along with nexial.enableEmail are both required for Nexial
to send out post-execution email notification.
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.mailSubject |
text | read/write |
NOTE: nexial.enableEmail MUST BE SET TO
true IN ORDER TO ACTIVATE THIS FEATURE.Customized/optional mail subject instead of the default one. The inclusion of data variable, Nexial Expression and built-in function is possible to achieve a highly dynamic and expressive email subject. However, this might not resolve to the desired value since this System variable is resolved in the beginning of the execution, not the end. Note that Nexial's post-execution email subject will STILL be prefixed with [nexial] to
indicate the source of such email - i.e. [nexial] your customized subject ...For example, 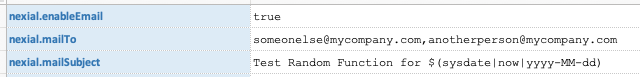 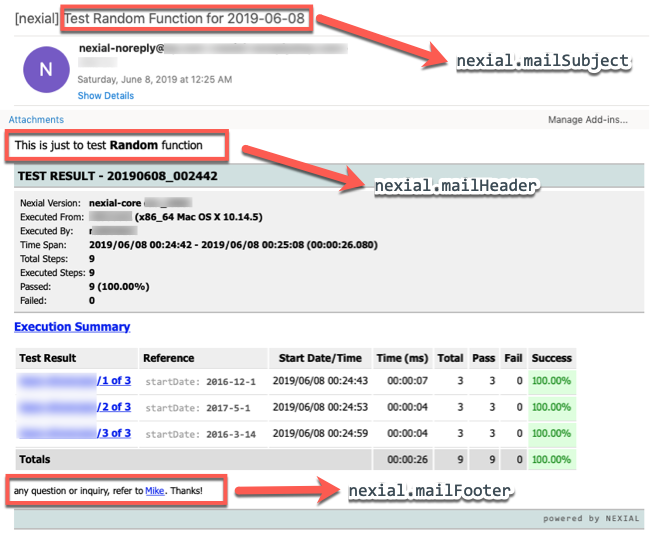 |
|||||||||||||
nexial.mailSubject.withSynopsis
|
boolean | true | read/write |
NOTE: nexial.enableEmail MUST BE SET TO
true IN ORDER TO ACTIVATE THIS FEATURE.Customize the system generated mail subject by adding a short "synopsis" of the overall execution. If this System variable is set to true (default), then Nexial will include either a postfix to the mail
subject:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.mailHeader |
text | read/write |
NOTE: nexial.enableEmail MUST BE SET TO
true IN ORDER TO ACTIVATE THIS FEATURE.
Customized/optional "header" message to be included in Nexial's post-execution email notification. The inclusion of data variable, Nexial Expression and built-in function is possible - as well as the use of HTML. However, this might not always resolve to the desired value since this System variable is resolved in the beginning of the execution, not the end. This can be useful towards including a custom-crafted "header" message to provide additional context of the execution. For example,   |
|||||||||||||
nexial.mailFooter |
text | read/write |
NOTE: nexial.enableEmail MUST BE SET TO
true IN ORDER TO ACTIVATE THIS FEATURE.
Customized/optional "footer" message to be included in Nexial's post-execution email notification. The inclusion of data variable, Nexial Expression and built-in function is possible - as well as the use of HTML. However, this might not always resolve to the desired value since this System variable is resolved in the beginning of the execution, not the end. This can be useful towards including a custom-crafted "footer" message to provide additional context of the execution. For example, 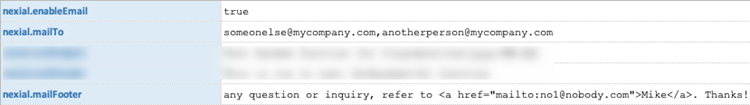  |
|||||||||||||
| For intra-step time tracking only. | ||||||||||||||||
nexial.timetrack.trackExecution
|
boolean | false | read/write |
This system variable is specified to track time taken for entire execution to complete. The time tracking
logs generated by this variable are stored alongside time-tracking logs for test steps.
For more information, see Time Tracking
Label for this will be run id which is in timestamp format and remark will be Execution ended.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.timetrack.trackScript
|
boolean | false | read/write |
This system variable is specified to track time taken for each script to complete. The time tracking logs
generated by this variable are stored alongside time-tracking logs for test steps. For more information,
see Time Tracking. Label for this will be script
name and remark will be Script ended.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.timetrack.trackIteration
|
boolean | false | read/write |
This system variable is specified to track time taken for each iteration to complete. The time tracking logs
generated by this variable are stored alongside time-tracking logs for test steps.
For more information on time tracking, see
Time Tracking. Label for this will be in the form of
scriptName#currentIteration and the remark will be Iteration ended.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.timetrack.trackScenario
|
boolean | false | read/write |
This system variable is specified to track time taken for each scenario to complete. The tracking logs
generated by this variable are stored alongside time-tracking logs for test steps.
For more information on time tracking, see Time Tracking
Label for this will be scriptName#scenario and remark will be Scenario ended.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.timetrack.format
|
text | read/write |
This system variable is to specify variety of formats for time tracking logs. Default format is
START_DATE|START_TIME|END_DATE|END_TIME|ELAPSED_TIME|THREAD_NAME|LABEL|REMARK.
For more information on time tracking, see Time Tracking
|
|||||||||||||
| For Nexial Expression only. | ||||||||||||||||
nexial.expression.OpenFileAsIs
|
boolean | false | read/write |
DEPRECATED SYSTEM VARIABLE NAME.
PLEASE SEE nexial.resolveTextAsIs INSTEAD.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.expression.resolveURL
|
boolean | true | read/write |
DEPRECATED SYSTEM VARIABLE NAME.
PLEASE SEE nexial.resolveTextAsURL INSTEAD.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.expression.web.alwaysNew
|
boolean | false | read/write |
When using WEB expression, one often starts by defining an
expression variable to gather each outcome from the subsequent
WEB operation calls. Towards the end of a WEB
expression, a common practice is to use the allPass
operation to evaluate the final "result" of the invoked WEB operations - true means all the
invoked operations were executed successfully. For example,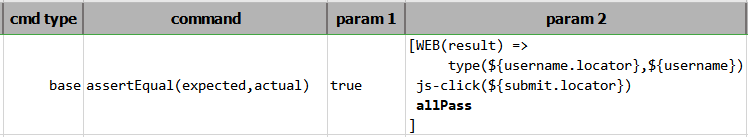 In the above example, the variable result holds the outcome of each of the operations within
the same WEB expression. It is possible to query to outcome of each operation via the standard
${...}.[property] syntax. See
Working with Execution Result
for more details.Suppose one would to reuse the same variable (in the above example, result) for another WEB
expression. In such case, Nexial will append the outcome of the operations in the subsequent WEB expressions
into the same variable, and thus "taint" the same variable with the execution of disparate WEB expressions.
At times, this may be intentional. However, quite often this is not the case.By default, Nexial will append the outcome of the operations in subsequent WEB expressions to the same variable (if the same variable name is used). To avoid this, one would need to either use a different variable name or to clear out the variable in question prior to the subsequent use of WEB expression. With this System variable - nexial.expression.web.alwaysNew - Nexial can now automatically
clear off the specified variable in a WEB expression. By setting this System variable as true,
each WEB expression will be started off with "clean slate". Therefore, subsequent use of the same variable
in WEB expression will not result in the outcome being grouped together across WEB expression.By default, this System variable is set to false.
|
||||||||||||
| For iteration-based testing only. | ||||||||||||||||
nexial.scope.iteration
|
ranges | 1 | read-only |
Specify the iteration or iteration range to execute. This can be expressed as number (each represent the
iteration index) or a number range. For example,
|
||||||||||||
nexial.scope.fallbackToPrevious
|
boolean | true | read-only | Specify the desired behavior when specific data is not defined. Set this to true means to traverse backward (in iteration) until the data is found in previous iteration. Setting it to false would enforce null to be used. | ||||||||||||
nexial.scope.currentIteration
|
integer | read-only | The index (1-base) of the iterations being executed. Note that this is not an indication that a specific iteration has completed or succeeded. | |||||||||||||
nexial.scope.currentIterationId
|
integer | read-only | The "id" of the iterations being executed. This is equivalent to the column position of the corresponding iteration in the datasheet. | |||||||||||||
nexial.scope.lastIteration
|
integer | read-only | The index (1-base) of the last completed iteration. This does not indicate whether the last iteration was completed with or without any failure. | |||||||||||||
nexial.scope.isFirstIteration
|
boolean | false | read-only |
true to indicate that the current iteration is the first iteration of the corresponding
script.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.scope.isLastIteration
|
boolean | false | read-only |
true to indicate that the current iteration is the last iteration of the corresponding
script.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.scope.refetchDataFile
|
boolean | true | read/write |
Determine whether Nexial should re-read the target data file per iteration or not. Sometimes it is
beneficial to re-fetch the target data file between iteration in case its content has been modified during
preceding iteration. This is the default behavior.
However, at times one might have the intention not to do so in order to preserve the changes made to data variables from one iteration to the next. In such case, one should set nexial.scope.refetchDataFile as false.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.scope.required.variables
|
text | read/write |
This System variable contains the comma separated list of data variables which needs to be defined before
start of an iteration. This will instruct Nexial to check whether value is assigned to those variables
before start of each iteration. If no value is found to be assigned to the specified variable(s), Nexial
will force user input to assign missing value for these variables via console prompt.
At times one might intend to assign one or more data variables at runtime (such as date or realtime data). One can use this System variable to enforce user input accordingly. For example, using web » open(url) in web
automation, URL is necessary to execute subsequent web commands. In such case, one would include the
respective variable as required using the nexial.scope.required.variables System variable.

During execution, if Nexial detect that such variable ( homepage.url) is not yet defined, a
console prompt will be rendered to solicit user's input: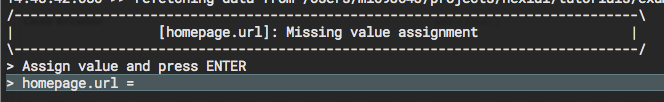
NOTE: nexial.scope.fallbackToPrevious
is applicable on the variables assigned from console prompt too.
Like most interactive feature, this variable is disabled - by design - when Nexial is executing in CI/CD environment (e.g. Jenkins). |
|||||||||||||
For base » repeatUntil(steps,maxWaitMs) command only.
|
||||||||||||||||
nexial.repeatUntil.index
|
integer | read-only |
This System variable keeps track of the loop occurrence for the current or last-used
base »
repeatUntil(steps,maxWaitMs).
During the execution of a repeat-until loop, Nexial will keep track of the loop occurrence (
in effect, the loop counter) and update this System variable accordingly. At the end of a
repeat-until loop, this System variable will continue to be available for the subsequent test
step.
It is, however, subject to being overwritten once the next instance of repeat-until loop
commence.
This System variable is 1-based (first loop is considered as 1).
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.repeatUntil.startTime
|
timestamp | read-only |
This System variable keeps track of the execution start time, in epoch, of a
base »
repeatUntil(steps,maxWaitMs)
instance. At the start of the next repeat-until loop, this System variable will be overwritten. |
|||||||||||||
nexial.repeatUntil.endTime
|
timestamp | read-only |
This System variable keeps track of the execution end time, in epoch, of a
base »
repeatUntil(steps,maxWaitMs)
instance. This System variable is not an indication of the status of a repeat-until loop; it
will be
updated at the end of a repeat-until loop regardless of its PASS/FAIL outcome. |
|||||||||||||
For io or csv
content comparison only.
|
||||||||||||||||
nexial.compare.textReport
|
boolean | true | read/write |
If true (default), content comparison will produce a text-based comparison report at the end.
The report is stored in the output directory (along with other test output) or in the cloud
(if nexial.outputToCloud is true) and will be downloadable via the execution output:
By default, this system variable is true. See
io »
compare(expected,actual,failFast)
for details.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.compare.jsonReport
|
boolean | false | read/write |
If true, content comparison will produce a JSON-based comparison report at the end. The report
is stored in the output directory (along with other test output) or in the cloud (if
nexial.outputToCloud is true) and will be downloadable ia the execution output:
By default, this system variable is false. See
io »
compare(expected,actual,failFast)
for details.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.compare.htmlReport
|
boolean | false | read/write |
If true, content comparison will produce an HTML comparison report at the end. The report is
stored in the output directory (along with other test output) or in the cloud (if
nexial.outputToCloud is true) and will be downloadable ia the execution output:
By default, this system variable is false. See
io »
compare(expected,actual,failFast)
for details.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.compare.reportMatch
|
boolean | false | read/write |
If true, content comparison will report each matching lines, in addition to reporting all mismatched
incidents. This can make the comparison report too tedious when comparing large files. See
io »
compare(expected,actual,failFast)
for details.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.io.eolConfig |
text | platform | read/write |
Control the end-of-line (EOL) character to use when writing content to a file via
io »
writeFile(file,content,append) or
io »
writeFileAsIs(file,content,append)
commands. Possible options are:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.io.copyConfig |
text | keepOriginal |
read/write |
Control copying of the existing file at the target location via
io »
copyFilesByRegex(sourceDir,regex,target) or
io »
copyFiles(source,target) or
io »
moveFilesByRegex(sourceDir,regex,target)
io »
moveFiles(source,target)
commands. Possible options are:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.io.matchRecursive
|
boolean | true | read/write |
Determine if Nexial should scan recursively when executing
io » saveMatches(var,path,fileFilter,textFilter)
command. By default, Nexial will scan the specified path recursively. If need be, one may set
this
System variable as false to instruct Nexial to scan only the specified directory.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.io.matchIncludeDirectories
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Determine if Nexial should include subdirectories when executing
io » saveMatches(var,path,fileFilter,textFilter)
command. By default, Nexial will scan only files under the specified path. If need be, one may
set this System variable as tue to instruct Nexial to scan both files and subdirectories under
the specified directory.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.io.matchExact |
boolean | false | read/write |
Determine if Nexial should perform file name matching based on "partial" or "exact" matching. This System
variable
impacts the following commands:
When set to true, Nexial will perform file name matches based on "exact" match. This means that
the file name would need to match exactly the specified regular expression to be considered eligible for the
corresponding command. For example, consider the following files:
FileA.txt FileB.txt B.txt A.txtSuppose the specified regular expression is [A-Z]\.txt, then only the last 2 files will be
considered as matches since only these 2 are exactly "one character followed by .txt".
However, if this System variable is set to false (default), then all 4 files would be
considered as matches since they all "partially" qualifies for the [A-Z]\.txt pattern.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.csv.maxColumns
|
integer | 512 | read/write |
Specify the maximum number of columns a CSV file/content can contain. This is used during the parsing
or construction of CSV data structure via the csv command or
via CSV expression. The default value is 512.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.csv.maxColumnWidth
|
integer | 4096 | read/write |
Specify the maximum number of character a column of a CSV file/content can contain. This is used during the
parsing or construction of CSV data structure via the csv command
or via CSV expression. The default value is 4096.
|
||||||||||||
| For JSON testing only. | ||||||||||||||||
nexial.json.treatJsonAsIs
|
boolean | true | read/write |
For JSON fragment extraction using command or expression, Nexial, by default, stores the resulting content
as close (or as compatible) to JSON as possible. This means that if the resulting content is a JSON array,
it will be stored like such:["Apple","Orange","Banana"]While this is perhaps more correct, it is at times more convenient to store the same information simply as a list, like so: [Apple,Orange,Banana]In doing so, we could further simplify the automation of parsing or comparison. The purpose of this System variable is to do exactly that. By default, this System variable is set to true - default behavior to keep extracted JSON fragments as "real" JSON as possible. When this
System variable is set to false, Nexial will remove double quotes (shown above) from the
extracted text data.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.json.lastCompareResults
|
json | read-only |
For json »
assertEqual(expectedJson,actualJson) only.Invoking json » assertEqual(expectedJson,actualJson) could reveal the structural differences between
the "expected" and "actual" JSON documents. Such differences are stored in yet another JSON document so that
one can further automate against the differences found. One can use this System variable to retrieve this
"diff" JSON.Note that one might want to consider using nexial.lastOutputLink to retrieve the file that
contains the "diff" JSON document.See nexial.json.compareResultsAsJSON,
nexial.json.compareResultsAsCSV and
nexial.json.compareResultsAsHTML for
report format. These report output optional are not mutually exclusive.
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.json.compareResultsAsJSON
|
boolean | true | read/write |
For json »
assertEqual(expectedJson,actualJson) only.Used to instruct Nexial on the report format of the comparison result (differences between expected and actual). By default, Nexial will generate the comparison result
as a JSON document, and link such file in the execution output. One may alter this System variable to
disable such default.See nexial.json.compareResultsAsCSV and
nexial.json.compareResultsAsHTML for other
report format. These report output optional are not mutually exclusive.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.json.compareResultsAsCSV
|
boolean | false | read/write |
For json »
assertEqual(expectedJson,actualJson) only.Used to instruct Nexial on the report format of the comparison result (differences between expected and actual). By default, Nexial will generate the comparison result
as a JSON document, and link such file in the execution output. One may alter this System variable to
disable such default and generate the comparison result as CSV instead.See nexial.json.compareResultsAsJSON and
nexial.json.compareResultsAsHTML for
report format. These report output optional are not mutually exclusive.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.json.compareResultsAsHTML
|
boolean | false | read/write |
For json »
assertEqual(expectedJson,actualJson) only.Used to instruct Nexial on the report format of the comparison result (differences between expected and actual). By default, Nexial will generate the comparison result
as a JSON document, and link such file in the execution output. One may alter this System variable to
disable such default and generate the comparison result as HTML instead.Note that the generated HTML is a basic HTML table where such table is assigned a style class named compare-result-table. One may choose to decorate this table by adding CSS to
table.compare-result-table. See json
»assertEqual(expectedJson,actualJson) for examples.See nexial.json.compareResultsAsJSON and
nexial.json.compareResultsAsCSV for
report format. These report output optional are not mutually exclusive.
|
||||||||||||
For external testing only.
|
||||||||||||||||
nexial.external.output
|
text | read-only |
This system variable reflects the filename of the output generated as a result of executing a
external »
runProgram(programPathAndParms) command.When executing the external » runProgram(programPathAndParms) command, Nexial also captures the output (standard
out) created by target external program. The captured output is then stored to the output directory
(as in $(syspath|output|fullPath)) and linked to the execution output.With the captured output filename derivable via this system variable, one can further the automation with regards the captured output. |
|||||||||||||
nexial.external.console
|
boolean | false | read/write | This system variable indicates that Nexial should push the console output (i.e. standard out) of the external programs it launches to the same console which Nexial logs. By doing so, users will be able to observe both the output from Nexial and the invoked external programs from the same console/terminal. | ||||||||||||
nexial.external.workingDirectory
|
text | read/write | This system variable specifies the location from where an external process would start. In some cases, it is important to specify the working directory (or some time it is referred to as the "starting directory") so that the program can run from its "home" location. Some program would use its working directory as the location to generate/reference temporal files. | |||||||||||||
For excel commands and
[EXCEL] expression only.
|
||||||||||||||||
nexial.excel.recalcBeforeSave
|
boolean | false | read/write |
This system variable instructs Nexial to perform formula recalculation before saving changes to an Excel
file.
Depending on the size of the target Excel and the number of formulae it contains, setting this System
variable
to true could potentially slow down the file saving process. By default, this System variable is
set to false.
Note that for [ EXCEL] expression, the target Excel
file is not automatically saved after each write operation
(e.g. EXCEL » writeAcross(start,value1,value2,value3,...). One would need to explicitly
invoke
the EXCEL » save(file,sheet,start) operation to trigger the recalculation.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.excel.retainCellType
|
boolean | false | read/write |
When writing data into Excel, Nexial writes them as text by default. This is generally acceptable. However,
at
times it is important to retain the cell type as found in the target Excel file. This is especially true if
the
affected cells are referenced by formulae found in the same Excel file. In such case, one can instruct
Nexial
to retain target cell data type by setting this System variable to true (default to
false).
Note that Nexial's attempt to retain the cell data type is limited. At this time it can handle NUMERIC, BOOLEAN and TEXT. Special data type of FORMULA,
DATE, OLE, etc. are currently not support.
|
||||||||||||
| For browser-based testing only. | ||||||||||||||||
nexial.browser |
text | firefox | read/write |
Determine the browser to use for test execution. The possible values are:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.delayBrowser
|
boolean | false | read-only |
Delay the initialization of web browser until the first command of
web » open() is invoked.
Generally one would not need to worry about this. Change this ONLY IF YOU KNOW WHAT YOU ARE
DOING!
|
||||||||||||
nexial.enforcePageSourceStability
|
boolean | false | read/write |
As of Nexial v3.9, this System variable has been set to false by default to improve overall
execution performance. It is determined that this System variable would be most applicable for web
applications that contain one or more active background AJAX calls after the current page is loaded. As
such, the "stability" of the corresponding web page might require the background AJAX calls to complete.
Setting this System variable to true would be helpful in such instance.
However, such behavior isn't common amongst most web application and hence this System variable is set to false by default.
Determine the browser page stability during test execution. Generally most of the modern web applications are rich in interactivity which require some background proceed to be completed when page gets loaded. But older or simpler web applications do not have such requirement. For such case, one can use this system variable to speed up test automation. true and will ensure that the web page in question is
stabilized before proceeding to next command.
false, this enforcement will be omitted. For example:
See nexial.waitSpeed for more control over this "stability
wait".
|
||||||||||||
nexial.waitSpeed |
integer | 3 | read/write | Determine how much time to wait for a dynamic page/response to stabilize before proceeding to next test step. This is set at a 400ms increment. | ||||||||||||
nexial.uiRenderWaitMs |
milliseconds | 3000 | read/write | The number of milliseconds to wait before taking a screenshot on current browser. This would allow the UI elements to "settle down". | ||||||||||||
nexial.pollWaitMs |
milliseconds | 30000 | read-only |
The time to wait for the impact caused by an action (such as click) to subside. In modern web-based
application, esp. those implemented with AJAX, not all the resulting elements (DOM, resource, etc.) are
available at the same time. As the browser concurrently downloads and renders each component, the position
and hierarchical order of these components might change as well. One should consider this configuration as a
"max wait time" – meaning that if the rendered content has settled or expected element is reachable prior
to this time, then Nexial will stop waiting and resume execution. Note that as per WebDriver specification, the poll wait time is only set once per initial use of a browser- specific webdriver instance. |
||||||||||||
nexial.web.unfocusAfterType
|
boolean | false | read/write |
For web application, it is not uncommon that the "type" event is recognized only after the target web
element has lost its focus. In other words, while entering text into a web element, no notification is
triggered to inform the web application (or its JavaScript event handler) that input has been entered into
a web element UNTIL the focus has been shifted from that web element. The need to
"unfocus-after-typing" hence becomes a pre-requisite for effective web automation for some web applications.
By default, this System variable is set to false. Setting it to true would enable
the "unfocus-after-typing" behavior, which effectively adds a TAB key after entering the specified input.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.clearWithBackspace
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Instruct Nexial to forcefully clear a textbox or textarea input via BACKSPACE key.This is not usually needed. However, some web application contains fairly persistent and intrusive event handler (or listener) that could circumvent the act of clearing out the corresponding input via the conventional way (i.e. Selenium's WebElement.clear()). Nexial can simulate user behavior by
issuing the BACKSPACE keystroke against any existing character found in the target INPUT
element. In some instances, this proves to be more effective, albeit possibly slower in performance.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.useReact
|
boolean | false | read/write |
This System variable indicates whether the AUT is built with ReactJs (or just React). React application often requires a
slightly different treatment when it comes to Web automation. By specifying this System variable as
true, Nexial can make the necessary adjustments accordingly.Specifically, if this System variable is set to true, then
By default, this System variable is set to false. If you are automating against a React
application, set this System variable to true.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.useComputedCss
|
boolean | false | read/write |
When set to true, this System variable instructs Nexial to determine CSS property value via
JavaScript - specifically via the `window.getComputedStyle()` function. As such, this technique has the
potential to derive at a CSS property value that is more consistent across all browsers.The default behavior is to use Selenium/WebDriver getElementValueOfCssProperty command, which
can differ slightly amongst driver implementations.If the target CSS property contains color property, then setting this System variable to true
would likely be a good idea (for consistency's sake).By default, this System variable is set to false.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.preemptiveAlertCheck
|
boolean | false | read/write |
(web commands only). When set to true, Nexial will check for the
presence of JavaScript alert/confirm/prompt dialog after a web command (such as click or type) and before
executing any of the waitFor... commands (such as
web »
waitForElementPresent(locator)).
If found, Nexial will harvest the text of the JavaScript dialog as nexial.lastAlertText, and
dismiss the dialog box as well, before proceeding on.While this behavior provides convenience, it is not without performance overhead. In order for Nexial to dismiss JavaScript dialog, it has to inquire via the underlying web driver against the browser in automation. Depending on the browser, this could take a few milliseconds to roughly half a second. For long-running automation, this overhead might be significant. By default, this System variable is set as false, which means Nexial will not proactively check
and
dismiss JavaScript dialog after a web command (e.g. click or type). Since most modern-day web applications
do not
employ the use of JavaScript dialog (such as alert('...')), it is likely a good idea to leave
this
feature off. Our rudimentary tests show a 12 - 20% time improvement when this feature is turned off, most
noticeably when running under IE.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.alwaysWait |
boolean | false | read/write |
DEPRECATED SYSTEM VARIABLE NAME.
PLEASE USE nexial.web.explicitWait INSTEAD.
When set to true, Nexial will enable explicit wait during Web automation with a poll of 10 ms
until the corresponding condition is reached or the value of
nexial.pollWaitMs is reached. This technique can help reduce
the use of implicit wait, which can be unreliable.The default is false.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.explicitWait
|
boolean | true | read/write |
When set to true (default), Nexial will enable
explicit wait during Web automation with a poll of 10 ms until the
corresponding condition is met or the value ofnexial.pollWaitMs
is reached. This technique can help reduce the use of implicit wait, which can be unreliable and is known
as a chief source of test flakiness.Technically speaking, Nexial implements fluent wait, which is essentially a more flexible form of explicit wait. Using this technique, we can overcome the infamous "stale element exception" as well. This System variable supersedes the now-deprecated nexial.web.always (since
Nexial v4.0)The default is true.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.pageLoadWaitMs
|
millisecond | 15000 | read/write |
Sets the amount of time (in millisecond) to wait for a page load to complete before considering the page
load event (such as web » open(url) is
considered as FAIL. If the timeout is negative, page loads can be indefinite.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.postCloseWaitMs
|
millisecond | 2000 | read/write |
Time allotted, in millisecond, to allow the system is settled down and process any clean up after
the
last browser window is closed. The default for this is 3000, which means the execution of
web » close() on the last browser window will add 3
seconds
by default to the overall execution time.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.incognito
|
boolean | true | read-only |
Determine if the target browser should be initialized by Nexial in incognito/private mode. The common
practice is to ALWAYS run browser in such mode to avoid residual side effects to the browser between
tests. The default is true.Due to a known/unresolved issue with chrome, if your tests requires resizing or maximizing target browser, the recommendation is to set this variable to false.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.windowSize
|
text | read-only |
IMPORTANT: This System variable is ignored for embedded Chrome, Electron or mobile browser automation
Specify the initial browser window size to be opened during test execution. Generally if windows size is not provided, the driver uses either previously-set or self-determined width/height during runtime.
In order to have a consistency, it is recommended to define browser height and width as desired initial
browser window size.For headless ( chrome.headless and firefox.headless) this is a
MUST.
If no window size is provided, Nexial will default the window size for the headless browser to
1200x900.For regular UI browser if window size not provided, it will execute whatever window size determined by the target browser found during execution. Dimension format as follows:
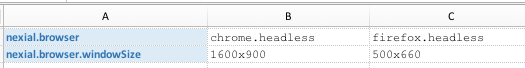
As of v4.5, Nexial now supports the use of one of these keyword to open the browser maximized:
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.browser.windowPosition
|
x,y | 0,0 | read-only |
IMPORTANT: This System variable is ignored for embedded Chrome, Electron or mobile browser automation
Specify the initial browser window position, in pixel, in relation to currently display (see nexial.targetDisplay for more details). The position
information is expected in the form of:x value in pixel,y value in pixelThe default value is 0,0, which means top-left corner of the assigned monitor. Specifying
640,1 on a screen resolution of 1280x960 would put the browser window on the right side of the
screen.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.downloadTo
|
text | $(syspath|out|fullpath) |
read-only |
APPLICABLE FOR CHROME AND FIREFOX BROWSERS ONLY. Specify the location to save any files downloaded from the current browser. By default, the download location is set to the output directory of the corresponding execution. This System variable is read during browser initialization. Any changes to this System variable after browser initialization will be ineffective until the execution is restarted. |
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.downloadPdf
|
boolean | true | read-only |
APPLICABLE FOR CHROME AND FIREFOX BROWSERS ONLY AT THIS TIME. Specify if a PDF document encountered during automation would be display in the browser or downloaded (to nexial.browser.downloadTo). By default, Nexial
will download PDF to disk rather than open the said PDF document to be opened in the current browser. In
many situations it is more beneficial to download the PDF. One can utilize the
pdf commands for additional automation.Note that when this System variable is set to false, PDF documents will open on the current
browser. By default, Nexial will download PDF documents to
nexial.browser.downloadTo, which, by default, is set
to $(syspath|out|fullpath).
|
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.forceJSClick
|
boolean | false | read/write |
By default, Nexial uses Selenium API (i.e. via WebDriver) for click event. This generally
works. However, with the combination of a certain browser and certain web application, timing sometimes work
against expectation. Such anomaly is especially noticeable with IE and AJAX-rich web applications (from
which timing might be less than predictable). To circumvent this issue, one may turn on the feature of
forcefully issuing click event via JavaScript by setting nexial.browser.forceJSClick to
true.Consequently, this feature is also effective as a workaround for IE to handle the click event on a target inside an iframe, which can be particularly problematic when the click event triggers a 'File Download' that in turn triggers a IE-only 'Download Notification' outside of the iframe. |
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.forceJSDoubleClick
|
boolean | false | read/write |
By default, Nexial uses Selenium API (i.e. via WebDriver) for double-click event. This
generally works. However, with the combination of a certain browser, web application and its underlying
UI framework, this fails at times. It's been known that WebDriver-based double-click automation on
Electron application and some React-based web application can fall trap to such issue. To circumvent this
issue, one may turn on the feature of forcefully issuing click event via JavaScript by setting
nexial.browser.forceJSDoubleClick to true. By doing so, Nexial will execute
JavaScript on the target application to trigger double-click event. |
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.geolocation
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Specify true to enable geolocation support on the target browser. This would enable
geolocation detection, which could possibly alter the behavior of the web application under test.Currently only the Chrome and Firefox browsers are support for this feature. |
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.geolocation.longitude
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Use this System variable, along with
nexial.browser.geolocation.latitude to
simulate a different geo location - a.k.a. location faking.To find the corresponding longitude and latitude via address, consider using the following websites: Get Lat Long from Address GPS Coordinates Currently only the Chrome and Firefox browsers are support for this feature. |
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.geolocation.latitude
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Use this System variable, along with
nexial.browser.geolocation.longitude to
simulate a different geo location - a.k.a. location faking.To find the corresponding longitude and latitude via address, consider using the following websites: Get Lat Long from Address GPS Coordinates Currently only the Chrome and Firefox browsers are support for this feature. |
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.meta
|
object | read-only | Metadata for the browser for the current execution. For more information, visit Browser Metadata. | |||||||||||||
nexial.browser.lang
|
string | read/write |
NOTE: THIS SYSTEM VARIABLE IS EFFECTIVE ON CHROME BROWSER ONLY. FUTURE VERSION OF NEXIAL WILL LIKELY SUPPORT OTHER BROWSERS.
Use this System variable to change the browser's language setting. By default, the browser is launched using the language setting of its underlying operating system. For the purpose of testing, it is sometimes useful to change the browser's language setting in order to evaluate its impact on the target web application. For example, by setting nexial.browser.lang to zh-TW, Google Search is rendered
in Chinese: For more ideas and technical details, visit the How to automate website in different languages side-by-side |
|||||||||||||
nexial.ignoreBrowserAlert
|
boolean | false | read-only | For browser-based testing only. Determine the behavior to used if an unexpected Alert is found. If set to true, unexpected alert will be ignored. | ||||||||||||
nexial.lastAlertText |
text | read-rewrite |
(webalert commands only). The text of the
last javascript alert found during test execution. For example: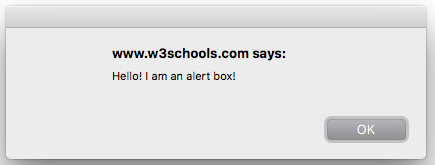
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.web.highlight
|
boolean | false | read/write |
RENAMED FROM THE OUTDATED nexial.highlight FOR CONSISTENCY AND PROPER NAMESPACING.
Highlight each web form element as an automation action is performed on it. These automation actions are typically some form of clicking or typing. "Mouseover" will not trigger such highlighting. Currently the highlight style is set to background:#faf557 (default for
nexial.web.highlight.style) for a period of
250ms (default for
nexial.web.highlight.waitMs). The "flashing yellow effect" (default style) is meant as a visual indicator of a test execution in progress. Here's an example (where the field Joe is highlighted):
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.highlight.waitMs
|
millisecond | 250 | read/write |
RENAMED FROM THE OUTDATED nexial.highlightWaitMs FOR CONSISTENCY AND PROPER NAMESPACING.
The amount of time, in milliseconds, before the highlight effect is removed and the style of target web element restored. This is only effective when nexial.web.highlight is set to true.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.highlight.style
|
text | background: #faf557 |
read/write |
The applicable CSS style to the target web element during highlighting. This is only effective when
nexial.web.highlight is set to true.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.toastDescription
|
boolean | false |
read/write |
ONLY APPLICABLE TO WEB AUTOMATION, OR AN EXECUTION WHERE THE WEB BROWSER IS ACTIVELY IN USE
This System variable specifies if Nexial should use the description of the current test step as "toast notification" on the current browser window. See web » toast(message,duration,darkMode) for more details. If set to true,
then Nexial will attempt to collect the description (Column B) of the current test step to create a toast
notification. If no description can be collected, or if there is no browser utilized within current
execution, then no toast notification will be generated. One may consider this turnkey feature as an easy
way to create on-the-fly narration on the browser whilst the target application is being automated or
tested. By default, this System variable is set to false.For further fine-tuning, see nexial.web.toastDescriptionWaitMs and
nexial.web.toastDescriptionDarkMode System variables.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.toastDescriptionWaitMs
|
number | 1500 |
read/write |
ONLY APPLICABLE TO WEB AUTOMATION, OR AN EXECUTION WHERE THE WEB BROWSER IS ACTIVELY IN USE
This System variable specifies that, if a toast notification should be displayed (see nexial.web.toastDescription), how long would such
notification be displayed. This System Variable specifies such time in milliseconds. By default, it is set
to 1500 (i.e. 1.5 second).
See web » toast(message,duration,darkMode) for more details.
For further fine-tuning, see nexial.web.toastDescription and
nexial.web.toastDescriptionDarkMode System variables.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.toastDescriptionDarkMode
|
boolean | true |
read/write |
ONLY APPLICABLE TO WEB AUTOMATION, OR AN EXECUTION WHERE THE WEB BROWSER IS ACTIVELY IN USE
This System variable specifies that, if a toast notification should be displayed (see nexial.web.toastDescription), if it should be
displayed in "dark" mode or "light" mode. Since different websites look differently, one may want to use
this System variable to adjust the toast notification to improve the overall UX. By default, it is set
to true (i.e. "dark" mode).
See web » toast(message,duration,darkMode) for more details.
For further fine-tuning, see nexial.web.toastDescription and
nexial.web.toastDescriptionDarkMode System variables.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.scrollIntoView
|
boolean | true | read/write |
During web automation, it is possible that the target web element might not be visible on the screen.
Perhaps it is below or above the viewing area of the host browser. To help clarify intent, it might be
a good idea to bring such web element into view before any automation is carried out upon it.
When this System variable is set to true (which is the default), Nexial will attempt to adjust
the position of target web element (like scrolling the page) such that it would be visible prior to carrying
out the automation. However, in some cases this preemptive "scrolling" might work against intended use as
some web elements might be too big to fit the available view area. In addition, the additional scrolling
could be considered unnecessary when automating via headless browser.
One can set this System variable to false to reduce such scrolling, which can also speed up
automation a bit.
This is applicable to
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.dragFrom
|
text | middle | read/write |
Set the starting point on the target element from which to initiate a "drag" movement. See
web » dragTo(fromLocator,xOffset,yOffset)
for more details.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.dragNative
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Determine if the web »
dragAndDrop(fromLocator,toLocator) and
web » dragTo(fromLocator,xOffset,yOffset) commands should be performed via native
mouse event (meaning: the actual "mouse-click-drag-move-then-drop") or via the WebDriver simulation
(default).
This is not often required (nor recommended) as setting the "native" mode will interrupt one's use of the mouse device during the execution of either aforementioned commands. Not so much of an issue when running one's automation via remote terminals. But this might result in some minor annoyance when automating via one's laptop/workstation. Running the drop-and-drop functionality using native mouse event is needed at times. This is especially true when the target web application drastically change either the source or the target web element during the drag-and-drop event, or if a new web element is generated (often as a visual cue) during the drag-and-drop. By default this System variable is set to false. When setting this System variable to true, one might want to consider the following System variables as well: |
||||||||||||
nexial.web.dragNativeXOffset
|
integer | 0 | read/write |
Instruct Nexial to apply additional offset to the x-position. Only applicable when
nexial.web.dragNative is set to true.
The idea behind this System variable is to provision control over one's browser. For example, one may have the browser configured with a thicker border. Using this System variable to take into account the additional value that the browser might have taken in the x-axis. By default this System variable is set to 0.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.dragNativeYOffset
|
integer | 80 | read/write |
Instruct Nexial to apply additional offset to the y-position. Only applicable when
nexial.web.dragNative is set to true.
The idea behind this System variable is to provision control over one's browser. For example, one may have the browser configured additional icons or a "taller" title bar. Using this System variable to take into account the additional value that the browser might have taken in the y-axis. By default this System variable is set to 80 since almost all browser would have title bar,
the address/location bar, etc.
|
||||||||||||
For web » save...AsCsv() commands only.
|
||||||||||||||||
nexial.web.saveGrid.deepScan
|
boolean | false | read/write |
ONLY APPLICABLE TO THE FOLLOWING COMMANDS:
saveTableAsCsv(locator,nextPageLocator,file)saveDivsAsCsv(headers,rows,cells,nextPage,file)<th>,
<td>, or <div>) with text content will be captured into CSV. Data cell
with web elements such as checkbox, drop down list (a.k.a. pick list), text box, image, etc. are thus
ignored.By setting this System variable to true (default is false), Nexial will activate
additional scanning of these non-text web elements and capture the corresponding metadata into CSV.
Precisely which metadata to capture will be determined by the additional System variables:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.saveGrid.header.input
|
text | name |
read/write |
ONLY APPLICABLE TO THE FOLLOWING COMMANDS:
saveTableAsCsv(locator,nextPageLocator,file)saveDivsAsCsv(headers,rows,cells,nextPage,file)Note that nexial.web.saveGrid.deepScan must be set to true in order for System
variable to take effect.
When "deep scan" is activated (see nexial.web.saveGrid.deepScan), one can determine what Nexial should capture when it encounters HTML form element such as:
save...AsCsv() commands. The default value for this
System variable is name.Possible choices are:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.saveGrid.header.image
|
text | type |
read/write |
ONLY APPLICABLE TO THE FOLLOWING COMMANDS:
saveTableAsCsv(locator,nextPageLocator,file)saveDivsAsCsv(headers,rows,cells,nextPage,file)Note that nexial.web.saveGrid.deepScan must be set to true in order for System
variable to take effect.
The default value for this System variable is type, which will have the value
image.
Possible choices are:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.saveGrid.data.input
|
text | state |
read/write |
ONLY APPLICABLE TO THE FOLLOWING COMMANDS:
saveTableAsCsv(locator,nextPageLocator,file)saveDivsAsCsv(headers,rows,cells,nextPage,file)Note that nexial.web.saveGrid.deepScan must be set to true in order for System
variable to take effect.
Possible choices are:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.saveGrid.data.image
|
text | type |
read/write |
ONLY APPLICABLE TO THE FOLLOWING COMMANDS:
saveTableAsCsv(locator,nextPageLocator,file)saveDivsAsCsv(headers,rows,cells,nextPage,file)Note that nexial.web.saveGrid.deepScan must be set to true in order for System
variable to take effect.
Possible choices are:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.saveGrid.data.trim
|
boolean | true | read/write |
ONLY APPLICABLE TO THE FOLLOWING COMMANDS:
saveTableAsCsv(locator,nextPageLocator,file)saveDivsAsCsv(headers,rows,cells,nextPage,file)Determine if the captured data should be trimmed before saving to CSV file. Default is true.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.saveGrid.end.trim
|
boolean | false | read/write |
ONLY APPLICABLE TO THE FOLLOWING COMMANDS:
saveTableAsCsv(locator,nextPageLocator,file)saveDivsAsCsv(headers,rows,cells,nextPage,file)Determine if the CSV file should be ended with a line feed or not. This can help to shape the CSV file to ease the analytical or comparison work to follow. The default is false, which means that a
line feed will be added to the end of the CSV file.
|
||||||||||||
| Browser-specific configuration. | ||||||||||||||||
nexial.browser.safari.useTechPreview
|
boolean | false | read-only |
Applicable only when nexial.browser is set to safari.Instruct Nexial to use the Safari Technology Preview if this system variable is set to true, otherwise use the release version of Safari (default). Set this system variable to
true ONLY the executing host has
Safari Technology Preview properly installed.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.electron.forceTerminate
|
boolean | false | read/write |
For Electron application only
For electron application, it is possible to forcefully terminating the application (AUT) when
closeAll()true (default is
false).
|
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.logElectron |
boolean | false | read/write |
Enable/Disable webdriver logging when automating against an Electron application. The
nexial.browser System variable must be set to electron. When enabled, Nexial will
create under the log directory of the execution output directory a log file named as
electron-[application].log, where [application] is the name of the application
under test. This file will contain the webdriver logs during automation, and will be linked in the
#summary tab of the execution report (.xlsx) under the logs section.While not usually needed, webdriver log contain be very useful towards troubleshooting and debugging intercommunication issues between webdriver and AUT. |
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.logElectronVerbose
|
boolean | false | read/write |
ONLY APPLICABLE WHEN nexial.browser.logElectron IS SET TO trueEnable/Disable verbose webdriver logging when automating against an Electron application. By default, this System variable is false.While not usually needed, turning on verbose mode might be useful towards troubleshooting and debugging intercommunication issues between webdriver and AUT. |
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.logChrome
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Enable/Disable webdriver logging when automating against Chrome browser. The nexial.browser
System variable must be set to chrome or chrome-headless. When enabled, Nexial
will create under the log directory of the execution output directory a log file named as
chrome-browser.log. This file will contain the webdriver logs during automation, and will be
linked in the #summary tab of the execution report (.xlsx) under the logs
section.While not usually needed, webdriver log contain be very useful towards troubleshooting and debugging intercommunication issues between webdriver and the Chrome browser. |
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.logEdge
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Enable/Disable webdriver logging when automating against Microsoft Edge (chromium) browser. The
nexial.browser System variable must be set to edgechrome. When enabled, Nexial
will display the log generated by the Edge browser on the console, as well as the Nexial log file in the
log directory under the output directory.While not usually needed, webdriver log contain be very useful towards troubleshooting and debugging intercommunication issues between webdriver and the Chrome browser. |
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.userData
|
text | read-only |
Specify the user profile directory for the currently specified browser (via
nexial.browser). The user profile usually store cookies, caches and user preferences, which
can be used to test various scenarios such as "repeated visits" or "first-time visitor". Note that:
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.forceIE32 |
boolean | false | read-only |
Applicable only for automating Internet Explorer. This system variable instructs Nexial on which version of IEDriverServer to use for Internet Explorer. IEDriverServer is a resident program that translates Selenium commands (sent through Nexial) into automation events on Internet Explorer. Setting this system variable to true (default) would force the use the 32-bit version of IEDriverServer;
false would instruct Nexial to use the 32-bit version for the 32-bit Windows OS and 64-bit
version for 64-bit Windows OS.It has come to light that Internet Explorer in pre-Windows10 installation are NOT truly 64-bit. The Internet Explorer "shell" program is a 64-bit process - meaning the main window, the address bar, navigation buttons, menu, etc.). However the individual tabs - where the web page content is rendered - are still 32-bit process. As such, if we use the 64-bit IEDriverServer process, each interaction to the web page would cause an additional execution buffering and translation between the 64-bit and 32-bit instructions. This means that using the 64-bit IEDriverServer on pre-Windows10 Internet Explorer WILL BE SLOWER, in fact, much slower, than using 32-bit IEDriverServer. For this reason, this system variable can help by forcing the use of the 32-bit IEDriverServer to circumvent the additional processing needed to toggle between 32-bit and 64-bit instructions. By default, this system variable is set to false since it appears that the latest version of
IEDriverServer (3.5.1.1, as of 2017/09/01) has corrected the 'bit' issue.This system variable is marked as read-only because it is only read once during startup.
Further changes to this system variable during execution would have no impact to the execution.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.browser.ie.requireWindowFocus
|
boolean | false | read-only |
Applicable only for Internet Explorer Browser.
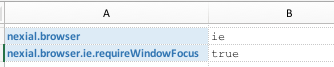
|
||||||||||||
webdriver.ie.driver |
text | read-only |
Applicable only for automating Internet Explorer. The location of the IE driver binary (ie IEDriverServer). By default, Nexial will determine the appropriate version of IEDriverServer to use, from one of the ones distributed as part of Nexial distribution. However, if for some reason you see the need to use a different IEDriverServer.exe, then use this
system variable to force the use of an out-of-distribution IEDriverServer.For more detail, see https://github.com/SeleniumHQ/selenium/wiki/InternetExplorerDriver This system variable is marked as read-only because it is only read once during startup.
Further changes to this system variable during execution would have no impact to the execution.
|
|||||||||||||
webdriver.ie.driver.loglevel
|
text | FATAL |
read-only |
Applicable only for automating Internet Explorer. Specifies the level at which logging messages are output. Valid values are FATAL,
ERROR,
WARN, INFO, DEBUG, and TRACE. Defaults to
FATAL.For more detail, see https://github.com/SeleniumHQ/selenium/wiki/InternetExplorerDriver This system variable is marked as read-only because it is only read once during startup.
Further changes to this system variable during execution would have no impact to the execution.
|
||||||||||||
webdriver.ie.driver.logfile
|
text | read-only |
Applicable only for automating Internet Explorer.
Specifies the full path and file name of the log file. For more detail, see https://github.com/SeleniumHQ/selenium/wiki/InternetExplorerDriver This system variable is marked as read-only because it is only read once during startup.
Further changes to this system variable during execution would have no impact to the execution.
|
|||||||||||||
webdriver.ie.driver.silent
|
boolean | false | read-only |
Applicable only for automating Internet Explorer. Suppresses diagnostic output when the IE driver is started. For more detail, see https://github.com/SeleniumHQ/selenium/wiki/InternetExplorerDriver This system variable is marked as read-only because it is only read once during startup.
Further changes to this system variable during execution would have no impact to the execution.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.secureBrowserStack
|
boolean | true | read-only |
Applicable only for automating on BrowserStack By default, connection to BrowserStack is secured via HTTPS connection. There are situations where this might not be desirable. Nexial can forcefully connect to BrowserStack via non-secured HTTP protocol if this System variable is set to false. Note that the availability and reliability of the BrowserStack
connections (secured or otherwise) is not controlled via Nexial. This System variable is only read once
at the start of the execution; changing its value during execution will have no impact.By default, this System variable is set to true.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.web.secureCrossBrowserTesting
|
boolean | true | read-only |
Applicable only for automating on CrossBrowserTesting (CBT) By default, connection to CrossBrowserTesting is secured via HTTPS connection. There are situations where this might not be desirable. Nexial can forcefully connect to CrossBrowserTesting via non-secured HTTP protocol if this System variable is set to false. Note that the availability and reliability
of the CrossBrowserTesting connections (secured or otherwise) is not controlled via Nexial. This System
variable is only read once at the start of the execution; changing its value during execution will have
no impact.By default, this System variable is set to true.
|
||||||||||||
For image-based testing (image commands) only.
|
||||||||||||||||
nexial.imageTolerance |
decimal | 0 | read/write |
For image commands only. Determine the amount of tolerance (0 to 100) when comparing two image
artifacts. 0 means "zero-tolerance".
|
||||||||||||
nexial.imageDiffColor |
text | red | read/write |
For image commands only. Determine the color for highlighting difference when comparing two
image artifacts. Available colors for highlighting are red, yellow,
blue, green, black, white.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.image.trimBeforeDiff
|
boolean | false | read/write |
For image commands only. Determine the images to be trimmed before comparing or not. Default is
false. To trim off spaces from images before comparing, set this variable to true.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.image.trimColor |
text | 255,255,255 | read/write |
For image commands only. Determine the color of trimming off spaces before comparing two
image artifacts. Default RGB color code of trimming spaces is 255,255,255, which is white. One
can provide their own color code as RGB values separated by comma (,). Here are a few examples:
|
||||||||||||
For ws commands only.
|
||||||||||||||||
nexial.ws.connectionTimeout
|
milliseconds | 300000 | read/write | Determine the connection timeout value (in milliseconds) until a connection is established. A timeout value of zero is interpreted as an infinite timeout. Default is 5 minutes. | ||||||||||||
nexial.ws.readTimeout |
milliseconds | 300000 | read/write | Determine the socket timeout value when reading response payload from either a reused or new connection. Default is 5 minutes. | ||||||||||||
nexial.ws.keepAlive |
boolean | true | read/write |
Set to true to turn onsocket keep-alive, which has
performance benefits via reusing the same connection over multiple
requests.
The default value of this System variable is true
|
||||||||||||
nexial.ws.enableRedirects |
boolean | false | read/write | Determines whether redirects should be handled automatically. | ||||||||||||
nexial.ws.enabledExpectContinue
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Determines whether the 'Expect: 100-Continue' handshake is enabled for HTTP methods with
payload body (such as POST and PUT). The purpose of the 'Expect: 100-Continue' handshake is
to allow a client that is sending a request message with a request body to determine if the origin
server is willing to accept the request (based on the request headers) before the client sends the
request body.The use of the ' Expect: 100-continue' handshake can result in a noticeable performance
improvement for entity enclosing requests (such as POST and PUT) that require the target server's
authentication.' Expect: 100-continue' handshake should be used with caution, as it may cause problems with
HTTP
servers and proxies that do not support HTTP/1.1 protocol.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.ws.allowCircularRedirects
|
boolean | false | read/write | Determines whether circular redirects (redirects to the same location) should be allowed. The HTTP specification is not sufficiently clear whether circular redirects are permitted, therefore they can be optionally enabled. | ||||||||||||
nexial.ws.allowRelativeRedirects
|
boolean | true | read/write |
Determines whether relative redirects should be rejected. An older HTTP 1.1 specification requires the
location value be an absolute URI. But since most browsers tolerates relative URI,
the
said HTTP specification hence relaxed such restriction. Set this configuration to true
to simulate modern browsers' default behavior.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.ws.requestPayloadCompact
|
boolean | false | read/write | Determine if request query string or request body should be trimmed (beginning and ending spaces removed) prior to it being sent to target URI. | ||||||||||||
nexial.ws.requestPayloadAsRaw
|
boolean | false | read/write |
This System variable is applicable when the corresponding request body is expressed as a fully qualified
file
path. Nexial has the capability to use such file content in binary form such as the case for images or PDF,
or as UTF-8 text form such as JSON, XML or plain text. By default, Nexial will determine the file content
type based on preceding HTTP header (set via ws »
header(name,value) command). One may override this default behavior to enforce a specific
file type treatment via this System variable. Setting it to true means that Nexial should set
up request payload content as binary (meaning charset or character encoding).Note that by setting this System variable to true, Nexial will:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.ws.header.* |
text | read/write |
Execution-bound HTTP header(s) to be used for each HTTP request (regardless of method). This is a
convenience mechanism since one would only need to define a set of common HTTP headers in the data file
for them to take effect for all HTTP requests issued within the same test execution. For example, one
may specify a list of common HTTP headers in the data file like this:
For a list of common/standard HTTP header names and related information, consult this link. |
|||||||||||||
nexial.ws.digest.user
|
text | read/write |
Authenticate HTTP interaction via the digest authentication scheme as defined in RFC 2617. All but
nexial.ws.digest.nonce are required configuration parameters to activate such authentication.
Any required configuration missing would not trigger such authentication.
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.ws.digest.password
|
text | read/write | ||||||||||||||
nexial.ws.digest.realm
|
text | read/write | ||||||||||||||
nexial.ws.digest.nonce
|
text | read/write | ||||||||||||||
nexial.ws.basic.user |
text | read/write | Authentication HTTP interaction via the basic authentication scheme as defined in RFC 2617. This authentication scheme is insecure, as the credentials are transmitted in clear text. Both of these parameters are required to trigger such authentication. | |||||||||||||
nexial.ws.basic.password
|
text | read/write | ||||||||||||||
nexial.ws.multipart.spec
|
text | standard | read/write |
APPLICABLE FOR ws »
upload(url,body,fileParams,var) COMMAND ONLY.When performing a file upload operation on an API call, sometimes it is beneficial (even necessary) to fine-tune the underlying HTTP construct in order to yield the desired effect. The file upload operation has undergone various specification changes over the year. The latest specification is RFC 6532. Subsequently, Nexial is using this RFC 6532 as the default "mode" for file upload operation for API testing. These "modes" essentially controls how Nexial constructs the HTTP request, particularly the HTTP headers for each of the multipart content.
When in doubt, start with the default ( standard) mode. Chances are it will work as expected.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.ws.multipart.charset
|
text | read/write |
APPLICABLE FOR ws »
upload(url,body,fileParams,var) COMMAND ONLY.While performing a file upload operation on an API call, sometimes it is beneficial (even necessary) to explicitly use a specific character set. One can use this System variable to instruct Nexial on the specific character set to use. If none is defined, none will be specified during the construction of the corresponding HTTP request. For example, nexial.ws.multipart.charset=UTF-8 would instruct Nexial to add
; charset=UTF-8 to the end of the multiple request header, like this:Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=oasidASLD...; charset=UTF-8
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.ws.logDetail
|
boolean | false | read/write |
When set to true (default is false), Nexial will record the request and response
detail for each API call made via ws commands. See the
ws Logging section for more details.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.ws.logSummary
|
boolean | false | read/write |
When set to true (default is false), Nexial will record summary information for
each API call made via ws commands. See the
ws Logging section for more details.
|
||||||||||||
For ws.async commands only.
|
||||||||||||||||
nexial.ws.async.shutdownWaitMs
|
millisecond | 180000 | read/write | In order to support the download to file that might potentially take longer than the execution time, Nexial will attempt to wait for the asynchronous HTTP invocations (if any) to complete before shutting down. The amount of such wait time is by default set to 180000 (3 minutes). One may override the default with another value, in millisecond, to possible speed up or prolong the shutdown event. | ||||||||||||
For desktop-based (desktop commands) testing only.
|
||||||||||||||||
nexial.desktopNotifyWaitMs
|
millisecond | 3000 | read/write | DEPRECATED SYSTEM VARIABLE. PLEASE USE nexial.desktop.notifyWaitMs instead | ||||||||||||
nexial.desktop.notifyWaitMs
|
millisecond | 3000 | read/write |
Specify the time to allow for a taskbar-based notification to stay visible. Such notification would display
log information as issued by the desktop commands, and they are displayed as a
"balloon".
|
||||||||||||
nexial.desktop.fullScreenCapture
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Specify if screenshot should be taken for the entire desktop or only limit to the target AUT.
If true, the screen capture will capture the entire desktop, possibly including other
applications and windows. If false, the screen capture will limit to the dimension of
the target AUT.If configuration can be useful when an application generates alert or modal dialog boxes that should be captured as test artifact. If such is the case, set this configuration to true.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.desktop.autoscan.verbose
|
boolean | false | read-only |
Set to true to enable additional logging during the
autoscanning process. This is
generally not required, but may provide some insights for troubleshooting purpose.Note that this System variable is only read once during the start of execution. Changes to this System variable during execution will not alter the logging behavior. By default, this System variable is set to false.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.desktop.autoClearModalDialog
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Set to true to automatically dismiss any modal dialog that shows up during automation as a
result of a click..., doubleClick..., clear... or
type...
commands.During automation, there are occasions where the target application would render a modal (meaning: blocking) dialog component - usually for the purpose of warning or to solicit user confirmation - after a certain action is performed. Nexial can automatically dismiss such dialog component and thus allow the automation to continue without user intervention. If this is the desired behavior, then one should set this System variable to true. The default value of this System variable is false.Note that automatically dismissing a dialog component might not always be the right course of action. There are situations where one should deliberately select the appropriate button presented in a dialog component. For example: 
When possible, one should consider explicitly automate the interaction with such dialog component, when possible. |
||||||||||||
nexial.desktop.explicitWait
|
boolean | true | read/write |
Nexial supports both implicit wait and explicit wait
(more technical details on waits) for desktop automation, much like how the
same is perceived for web automation. By using the explicit wait strategy, one would likely experience a
simpler automation scripting process and a more stable execution:
|
||||||||||||
nexial.desktop.simulateClick
|
boolean | false | read/write |
At times, the clicking of a desktop component such as a button would trigger the rendering of a modal
component (such as a dialog), like this: Depending on how the modal component is rendered, this can be an issue and the corresponding command might fail. If you are facing issue where the clicking of a component renders another modal component, and such rendering is causing the corresponding step to fail, then setting this System variable to true may help.Essentially, setting this System variable to true instructs Nexial to "simulate" the click rather than generating a "real" mouse click event. Using simulated click has the following effects:
clearModalDialog(var,button) command to dismiss the modal component.Note this System variable can impact the following commands: In addition, if one uses AutoScanning, then it's worth noting that a similar setting can be configured for an individual component instead of the entire execution. For example,
"Lock": {
"type": "DesktopElement",
"xpath": "...",
"controlType": "ControlType.Button",
"name": "Lock",
"automationId": "...",
"elementType": "Button",
"label": "Lock",
"extra": {
"nexial.desktop.simulateClick": true
}
}
See one of the above command links for more details.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.desktop.table.clickBeforeEdit
|
boolean | true | read/write |
When automating the editing of a table cell (desktop application only), it is often a good idea to bring
focus to the target row or cell prior to commencing the editing. This is the default behavior for Nexial
when executing desktop »
editTableCells(row,nameValues), Nexial will, by default, click on the target table row -
thus bringing such row to focus - and then proceed to enter specified data to target cells. However, there
might be situation where this initial click is not necessary or desirable. In such situation, one can
turn off the default behavior:nexial.desktop.table.clickBeforeEdit=falseNote that this System variable cannot be overridden individually for each desktop grid configuration (i.e. auto-scanned JSON file). One can add this System variable in the "extra" section of the
corresponding JSON file to customize this behavior, like this:
"grid": {
"type": "DesktopHierTable",
... ...
"extra": {
"nexial.desktop.table.clickBeforeEdit": true
},
... ...
}
|
||||||||||||
nexial.desktop.table.tabAfterEdit
|
boolean | false | read/write |
When automating the editing of a table cell (desktop application only), it might be a good idea to
"tab out" of a cell after editing so that the AUT can carry out the appropriate "out of focus" event for
that cell. For example, the application might invoke a verification API against the input, or execute
a lookup routine to populate additional fields. By configuring this System variable to "tab out" after
each edit, one might be able to simulate the intended user experience more accurately.
This System variable impacts only "table edit" related commands such as
desktop »
editTableCells(row,nameValues). By default, this System variable is set to
false.Note that this System variable cannot be overridden individually for each desktop grid configuration (i.e. auto-scanned JSON file). One can add this System variable in the "extra" section of the
corresponding JSON file to customize this behavior, like this:
"grid": {
"type": "DesktopHierTable",
... ...
"extra": {
"nexial.desktop.table.tabAfterEdit": true
},
... ...
}
|
||||||||||||
nexial.desktop.useTypeKeys
|
boolean | false | read/write |
This System variable applies to the following commands:
true
(default is false).When this System variable is set to true, Nexial converts the text input parameters to
"keystrokes". Functionally this would be equivalent to
web »
typeKeys(os,keystrokes).Note that this System variable cannot be overridden by the desktop component configuration (i.e. auto-scanned JSON file). One can add this System variable in the "extra" section of the
corresponding JSON file to customize this behavior, like this:
"TextBox1": {
"type": "...",
... ...
"extra": {
"nexial.desktop.useTypeKeys": true
},
... ...
}
|
||||||||||||
nexial.desktop.useAsciiKey
|
boolean | false | read/write |
This System variable applies to the following commands:
Turn this System variable to true to instruct Nexial to use ASCII-based key mapping, instead
of the more-common
Unicode PUA (Private Use Area) code points (which, incidentally, is what Selenium is based on).This is at times necessarily, especially in the case of automating legacy applications. |
||||||||||||
nexial.desktop.dialogLookup
|
boolean | false | read/write | Specify if any uncertainty of showing up of dialog boxes while editing the desktop table cells. If any such dialog box comes up, Nexial will stop further editing the table cells and the step will be failed. | ||||||||||||
nexial.desktop.infragistics4Aware
|
boolean | false | read/write | Tune Nexial towards "awareness" of Infragistics v4 (and possibly beyond) component during autoscanning process. | ||||||||||||
nexial.winiumJoinExisting
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Determine if Nexial should "join session" with an existing Winium instance or create its own (i.e. new).
This configuration would only make sense to be set to true if nexial.winiumPort is also
specified (to the existing running Winium instance). Using both these configurations together can create an
efficient way to script development. By attaching to another active Winium instance (and thus a running
instance of the application under test), one could test out a sequence of test steps without restarting
the application each time.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.winiumPort |
integer | read-only | Specify the port to use (by Winium driver) when automating against a desktop application. Winium uses this port to communicate between Nexial and the Winium command processor. If none specified, Nexial will search for a random open port that is above 1024. | |||||||||||||
nexial.winiumSoloMode |
boolean | true | read/write |
Determine if Nexial should run the current AUT exe in "Solo" mode (default) - which means to reuse
existing instances if found. This means that one could forcefully configure the AUT to run as a single
instance, even when multiple desktop »
useApp(appId)
command was invoked. This is especially useful when dealing with an application that requires additional
time and resources to "startup". When subsequent desktop
» useApp(appId) command is invoked, Nexial will simply reuse the existing running
instance and thus save time.However, it is important to note that desktop » closeApplication() command will effectively be ignored. One would set this system variable
to false in order to terminate the running AUT instance. Example: 
|
||||||||||||
For database (rdbms commands) testing only.
|
||||||||||||||||
nexial.rdbms.packSingleRow
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Specify in the scenario where a single row is returned as a result of executing a SQL statement, whether
Nexial should pack the result set (i.e.the single row) by removing all NULL columns.This System variable is automatically disabled when multiple rows are returned. |
||||||||||||
For mobile (mobile commands) testing only.
|
||||||||||||||||
nexial.mobile.postActionWaitMs
|
integer | 0 | read/write |
Specify the amount of time, in millisecond, to wait after an action is performed on the target device. An
action can be aclick, or
double-click, or some
typing. Adjust this System variable to provide a more stable automation, especially for the less performant mobile apps. However, any value less than 250 would be ignored as such low value will likely make any impact during the execution. The default value of 0 means that Nexial will not artificially inject any
"pause" between actions.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.mobile.explicitWaitMs
|
integer | 5000 | read/write |
Specify the maximum amount of time, in millisecond, to wait a specified locator to be resolved. Commonly
known as explicit wait, this System variable specifies the maximum amount of time to wait for the target
element to be available for interruption. If both nexial.mobile.explicitWaitMs and nexial.mobile.implictWaitMs are specified,
the former would take precedence as it is usually prefer explicit wait over implicit wait.
|
||||||||||||
nexial.mobile.implicitWaitMs
|
integer | 0 | read/write |
Specify the time to wait before attempt to resolve an element against the specified locator. If the element
is not found, the corresponding step would be considered as FAIL. In most cases, it
is preferred to use explicit wait instead of implicit wait. Explicit wait is more flexible and allows for
better control against mobile applications with inconsistent performance.If both nexial.mobile.explicitWaitMs and nexial.mobile.implictWaitMs are specified,
the former would take precedence as it is usually prefer explicit wait over implicit wait.A value less than 200 (that is, 200 milliseconds) will be ignored. |
||||||||||||
nexial.mobile.sessionTimeoutMs
|
integer | 0 | read/write |
Specify the amount of time, in millisecond, that Appium should wait for a new command from its client
(i.e. Nexial) before assuming that the client has quit and ended the session. This is equivalent to the newCommandTimeout capability found in
Appium Desired Capabilities (Under General Capabilities / newCommandTimeout). Note that
Nexial expects the value of this System variable in millisecond (for consistency), and will convert it to
seconds for Appium.It might be a good idea to keep the value of this System variable fairly high (e.g. 900000,
or 15 minutes) during a Interactive session. Without the pressure of timing
out (from Appium) too often, one can interactively learn and try out various automation ideas
author the automation script without getting timed out too often.Default value for this System variable is 0 -- meaning, no time out. |
||||||||||||
nexial.mobile.hideKeyboard
|
boolean | true | read/write |
Instruct Nexial to hide the on-screen keyboard before automate typing via the
type(locator,type) command. Default
value for this System variable is true.
|
||||||||||||
For TMS integration only.
|
||||||||||||||||
nexial.tms.source
|
text | read/write |
Specify source tool for Test Management Service integration. As of now, supported TMS tools by Nexial
are:
service
integration
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.tms.url
|
text | read/write |
Specify URL of the TMS tool where Nexial test cases to be imported. For example,
service
integration
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.tms.username
|
text | read/write |
Specify username required to access TMS tool api provided by nexial.tms.source
This can be empty text for some of the tools which provides access tokens to access apis.To setup TMS integration, please go through service
integration
|
|||||||||||||
nexial.tms.password
|
text | read/write |
Specify password required to access TMS tool api provided by nexial.tms.source
This can be password or access token to access apis. For example, Azure requires PAT(Personal Access
Token)To setup TMS integration, please go through service
integration
|
|||||||||||||
Standard System Properties
As a Java application, Nexial supports a set of standard System properties that are common across operating systems. These properties are managed and exposed by the Java runtime, which might increase in number over time. Nexial, in turn, expose these properties so that they may be used as part of automation.
For example, should one do such in a Nexial script:
This will print out the user ID that executed the script.
One can consider these System properties as reflection of the current test harness (where Nexial runs). Below is the list of available System properties:
| property name | explanation | example |
|---|---|---|
file.separator |
The character used to separate files and directory. On Windows, this is usually \. On *NIX and
OSX, this would be / |
|
java.home |
Where the current Java runtime is installed | |
java.io.tmpdir |
Current temp directory. The actual directory differs from host to host, depending on how each machine is set up | |
java.version |
The version of the current Java runtime, include the minor and patch number | 1.8.0_152 |
line.separator |
The character(s) used as line separator. On Windows this is commonly implemented as the \r\n, while in *NIX and OSX it's the \n character | |
os.arch |
The operating system architecture of the current host | x86_64 |
os.name |
The short name of the current operating system |
Mac OS XWindows
|
os.version |
The operating system version | 10.12.6 |
os.hostname |
The machine name of this current host | |
user.country |
The country or region code of the user that executed Nexial | US |
user.dir |
a.k.a. Current working directory This is the directory where Nexial - ultimately Java - was run. In most cases this would be ${NEXIAL_HOME}/bin
|
|
user.home |
User home directory |
C:\Users\Administrator/Users/admin
|
user.language |
The language code of the user that executed Nexial | en |
user.name |
The user ID of the user that executed Nexial. | |
user.timezone |
The timezone of the operating system that executed Nexial | America/Los_Angeles |
nexial.version |
The version of the currently-running Nexial Automation | nexial-core 3.5_0996 |
Example:
Script (note that ${whoami} is defined as data variable with the value of
${user.name}):
Output:
BrowserStack-specific Properties
Applicable only when nexial.browser is set to browserstack.
For more information, visit the BrowserStack Integration
page.
| configuration | data type | default | read only? | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
nexial.browserstack.username
|
text | read/write | [REQUIRED] This is the username as found in https://www.browserstack.com/accounts/settings (login required). | |
nexial.browserstack.automatekey
|
text | read/write | [REQUIRED] This is the access key as found in https://www.browserstack.com/accounts/settings (login required). | |
nexial.browserstack.browser
|
text | chrome | read/write |
Specify the browser to use when executing browser-based automation on BrowserStack. Valid value would be
limited to what
BrowserStack can support. For example, Firefox, Safari, IE, Chrome, Opera, Edge.
|
nexial.browserstack.browser.version
|
text | latest stable | read/write | Specify the browser version to use when executing browser-based automation on BrowserStack. Valid value would be limited to what BrowserStack can support. |
nexial.browserstack.debug
|
boolean | true | read/write | As per BrowserStack documentation: Required if you want to generate screenshots at various steps in your test. |
nexial.browserstack.resolution
|
text | 1024x768 | read/write |
Set the resolution of target VM before beginning of your automation. Below is what BrowserStack
supports: Windows (XP,7): 800x600, 1024x768, 1280x800, 1280x1024, 1366x768, 1440x900,
1680x1050, 1600x1200, 1920x1200, 1920x1080, 2048x1536Windows (8,8.1,10): 1024x768, 1280x800, 1280x1024, 1366x768, 1440x900, 1680x1050,
1600x1200, 1920x1200, 1920x1080, 2048x1536OS X: 1024x768, 1280x960, 1280x1024, 1600x1200, 1920x1080Default: 1024x768
|
nexial.browserstack.app.buildnumber
|
text | read/write | Allow user to group a set of automation under a specific label that would represent a specific AUT build. | |
nexial.browserstack.enablelocal
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Required if you are testing against internal/local servers. Nexial will
automatically
download/execute the OS-specific BrowserStackLocal binary before executing your tests. This
is necessary to proxy the connections to the internal/local resources.
|
nexial.browserstack.terminatelocal
|
boolean | true | read/write |
NOTE: Only applicable when nexial.browserstack.enablelocal is set to true.When this System variable is set to false (default is true), Nexial will
omit the termination of any running BrowserStackLocal binary. This may be necessary when
executing multiple simultaneous tests within one host.To ensure proper clean up, one may utilize the external » terminate(programName) command to terminate any running
BrowserStackLocal binary when all the tests are complete.
|
nexial.browserstack.os
|
text | read/write |
OS you want to test. For example: WINDOWS, OS X
|
|
nexial.browserstack.os.version
|
text | read/write |
OS version you want to test. For example: Windows: XP, 7, 8, 8.1 and 10OS X: Snow Leopard, Lion, Mountain Lion, Mavericks, Yosemite, El Capitan, Sierra
|
|
nexial.browserstack.captureCrash
|
boolean | false | read/write | Capture additional details if an automation session should crash. |
browserstack.*
|
* | read/write | Nexial will pass on all BrowserStack-specific "capabilities" to BrowserStack during automation. See the Capabilities Reference page for the supported capabilities (search for "BrowserStack-specific capabilities") |
CrossBrowserTesting-specific Properties (CBT)
Applicable only when nexial.browser is set to crossbrowsertesting.
For more information, visit the CrossBrowserTesting
Integration page.
| configuration | data type | default | read only? | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
cbt.username |
text | read/write | [REQUIRED] This is the username found in Automation: Getting Started (login required). | |
cbt.authkey |
text | read/write | [REQUIRED] This is the Auth Key found in Automation: Getting Started (login required). | |
cbt.browserName |
text | read/write | [REQUIRED] The name of the browser to test. For a list of supported browsers, check out CBT's Selenium Automation Capabilities page or http://crossbrowsertesting.com/api/v3/selenium/browsers. | |
cbt.screenResolution |
text | read/write |
(OPTIONAL) The preferred resolution of the OS for automated testing. The default is `1366x768`. Only applicable for desktop browser. |
|
cbt.version |
text | read/write |
(OPTIONAL) The browser version to test. Default is latest.Only applicable for desktop browser. |
|
cbt.platform |
text | read/write |
(REQUIRED for desktop browser) OS for the target browser. Only applicable for desktop browser. |
|
cbt.deviceName |
text | read/write |
(REQUIRED for mobile browser) The target mobile device name. Only applicable for mobile browser automation. |
|
cbt.deviceOrientation |
text | read/write |
landscape or portrait (default).Only applicable for mobile browser automation. |
|
cbt.build |
text | read/write | (OPTIONAL) free-form description of the build version of the target application. | |
cbt.name |
text | read/write | (OPTIONAL) free-form description of your test. | |
cbt.record_video |
text | read/write |
(OPTIONAL) true (default) to start video recording of the target browser during test
(max length 10 minutes).
|
|
cbt.record_network |
text | read/write |
(OPTIONAL) true to record the network packages incurred by the test automation.
|
|
cbt.max_duration |
text | read/write | (OPTIONAL) Maximum test length in seconds. Use to refrain from timing out during long tests. Default is 30 minutes. | |
cbt.timezone |
text | read/write | (OPTIONAL) timezone set on the browser. A full list of values can be found here. | |
cbt.enablelocal
|
boolean | false | read/write |
Required if you are testing against internal/local servers.
Nexial will
automatically download/execute the OS-specific cbt_tunnels binary before executing your tests.
This is necessary to proxy the connections to the internal/local resources.
|
cbt.terminatelocal
|
boolean | true | read/write |
NOTE: Only applicable when cbt.enablelocal is set to true.When this System variable is set to false (default is true), Nexial will
omit the termination of any running cbt_tunnels binary. This may be necessary when
executing multiple simultaneous tests within one host.To ensure proper clean up, one may utilize the external » terminate(programName) command to terminate any running
cbt_tunnels binary when all the tests are complete.
|